Did you know that the average person spends about six months of their life waiting for red lights to turn green? While you're waiting, why not learn how to manage your trading risks effectively? In this article, we delve into the essentials of stop-loss strategies, highlighting their importance in protecting your investments. We’ll cover how to set the right stop-loss levels, explore common strategies for beginners, and discuss how to balance risk and reward effectively. Additionally, you’ll learn about the best methods for volatile markets, the impact of position size, and when to adjust your stop-loss orders. We’ll also address the psychological benefits of using stop-losses and how they can shield you from significant losses during market downturns. With insights from DayTradingBusiness, you'll be better equipped to navigate the complexities of trading while safeguarding your profits.
What is a stop-loss and why is it important?
A stop-loss is an order set to sell a security when it hits a specific price, limiting potential losses. It's important because it helps traders protect capital, prevent emotional decision-making, and maintain a balanced risk-reward ratio. Using a stop-loss ensures you exit losing trades quickly and preserve gains on successful trades.
How do I set the right stop-loss level?
Set your stop-loss where the potential loss matches your risk tolerance, typically a small percentage of your total capital. Use technical analysis to identify support or resistance levels, placing the stop just beyond them to avoid false triggers. Consider the trade’s volatility; avoid tight stops in volatile markets. Balance risk and reward by ensuring your stop-loss allows for enough room to breathe while protecting against major losses. Always test your stop-loss levels with backtesting or paper trading before applying live.
What are common stop-loss strategies for beginners?
Common stop-loss strategies for beginners include setting a fixed percentage loss (like 5-10%), placing stop-loss orders just below recent support levels, and using trailing stops that follow price gains to lock in profits while limiting losses. These methods help balance risk and reward by capping potential losses and allowing room for growth. Avoid emotional decisions by sticking to these predefined levels.
How can I balance risk and reward using stop-loss orders?
Set your stop-loss at a level that limits potential losses without cutting too close to the entry point, balancing risk and reward. Use a percentage-based stop-loss, like 2-3% of your capital, to control risk. Adjust your stop-loss as the trade moves in your favor to lock in gains while still protecting against reversals. Consider the trade’s volatility—wider stops for volatile stocks, tighter stops for stable ones. Aim for a risk-to-reward ratio of at least 1:2; for example, if you risk $100, target $200 profit. This way, even if some trades hit stop-losses, the successful ones can cover losses and grow your account.
What is the best stop-loss method for volatile markets?
Use a percentage-based stop-loss, like 1-2% of your trading capital, to limit losses in volatile markets. Alternatively, set a volatility-adjusted stop-loss using ATR (Average True Range) to adapt to market swings. Avoid tight fixed stops that get triggered by normal fluctuations; instead, give your trades room to breathe. Trailing stops also work well, locking in gains while allowing for market noise. The key is balancing enough protection without forcing premature exits during sudden price swings.
How does position size affect stop-loss effectiveness?
Position size directly impacts stop-loss effectiveness by determining how much you risk per trade. Larger positions mean smaller price movements can hit your stop, increasing risk of premature exit. Smaller positions give more room for price fluctuations, reducing the chance of being stopped out by normal market noise. Proper sizing ensures your stop-loss protects your capital without forcing you out too early, balancing risk and reward. If your position is too big, even small market swings can wipe out gains or cause unnecessary losses; too small, and your potential reward diminishes.
When should I move or adjust my stop-loss?
Move or adjust your stop-loss when the trade moves in your favor, locking in profits and reducing risk. Trail your stop-loss as the price rises (or falls for shorts) to protect gains without limiting upside. Consider tightening your stop if the market becomes volatile or if your original setup changes. Avoid moving your stop-loss just to avoid a small loss; base it on technical levels or key support/resistance. Adjust when new market information or price action indicates a shift in trend or increased risk.
How do trailing stop-loss orders work?
Trailing stop-loss orders automatically adjust as the price moves in your favor, locking in gains while limiting losses. When the asset's price rises, the stop-loss moves up proportionally; if it falls, the order triggers sell once it hits that new, lower level. This setup helps you stay in a trade to maximize upside but exit quickly if the market turns. It’s a flexible way to balance risk and reward, letting profits run while protecting against sudden downturns.
What are the risks of setting too tight or too loose stop-losses?
Setting a stop-loss too tight risks frequent small losses, causing you to get stopped out before a trade can turn profitable. Too loose, and you expose yourself to bigger losses, risking your entire account on a single bad move. Tight stops can lead to emotional trading and overtrading, while loose stops may wipe out your capital faster. The key is finding a balance that protects your downside without limiting potential gains.
How can I use stop-loss to protect profits?
Set your stop-loss slightly below your entry point or recent support level to lock in profits as the trade moves in your favor. Adjust the stop-loss upward as the price rises to secure gains while allowing room for normal market fluctuations. Use trailing stop-loss orders to automatically move your stop-loss higher as the price increases, protecting profits without limiting upside. This way, you lock in gains if the market reverses while still giving your trade room to grow.
What role does risk-reward ratio play in stop-loss placement?
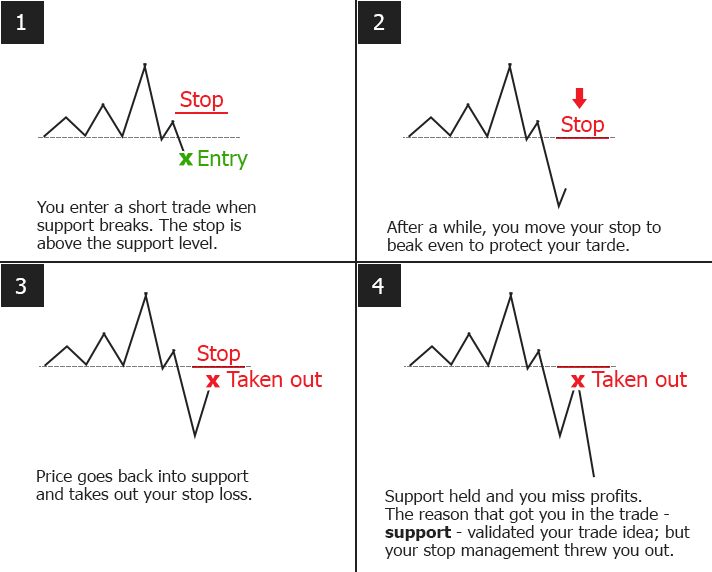
The risk-reward ratio guides where to place your stop-loss by ensuring potential gains outweigh potential losses. A favorable ratio, like 1:3, means setting a stop-loss where your loss is small compared to the target profit, helping you manage risk while aiming for meaningful rewards. It prevents setting stop-losses too tight, which could trigger early, and too loose, which exposes you to bigger losses. Ultimately, it balances the risk you're willing to take with the potential reward, making your stop-loss placement strategic and aligned with your trading goals.
How do different trading styles influence stop-loss strategies?
Different trading styles shape stop-loss strategies by defining risk tolerance and trade duration. Day traders set tight stops to limit quick losses in fast markets. Swing traders prefer wider stops to accommodate market swings over days or weeks. Position traders choose even larger stops, aiming for bigger moves but risking more per trade. Scalpers use very tight stops, sometimes just a few pips, to protect quick profits. Your trading style determines how much you’re willing to lose on each trade and how closely you monitor the market, balancing risk and reward accordingly.
Learn about How Do Institutional Traders Influence Day Trading Strategies?
What are the psychological benefits of using stop-losses?

Using stop-losses reduces emotional stress by limiting potential losses, helping traders stay calm during market swings. They prevent impulsive decisions driven by fear or greed, fostering disciplined trading. Stop-losses also boost confidence, making it easier to stick to your risk-reward plan. Knowing your downside is protected can reduce anxiety and improve overall mental clarity. This mental safety net encourages consistent, rational decision-making and preserves emotional well-being during volatile periods.
How does market volatility impact stop-loss decisions?
Market volatility makes stop-loss decisions tricky. When volatility spikes, prices swing wildly, risking premature stop-loss triggers. Traders might tighten stops to protect gains or loosen them to avoid being stopped out during normal fluctuations. High volatility requires more flexible stop-loss placement to balance avoiding losses and allowing room for market moves. Conversely, low volatility allows tighter stops, limiting potential losses without risking false triggers. Adjusting stop-loss levels based on volatility helps manage risk while capturing reward opportunities.
Can stop-loss strategies prevent large losses during market crashes?
Stop-loss strategies can limit large losses during market crashes by automatically selling assets when prices drop to a set level. They act as a safety net, preventing emotions from causing bigger losses. However, in fast, sharp crashes, stop-loss orders may trigger prematurely or at unfavorable prices. So, while they help manage risk, they can't guarantee avoiding all big losses in extreme market downturns.
Conclusion about How to balance risk and reward with stop-loss strategies
Incorporating effective stop-loss strategies is crucial for managing risk and reward in trading. By understanding how to set appropriate levels, adjust for market volatility, and leverage different stop-loss methods, traders can safeguard profits and minimize losses. The right balance enhances decision-making and supports overall trading success. For more in-depth insights and guidance on optimizing your trading strategies, look to DayTradingBusiness.
Learn about How to adapt stop-loss risk strategies to different markets