Did you know that even the smartest traders can fall victim to cognitive biases, sometimes making decisions that would make a goldfish look rational? In this article, we dive deep into how these biases influence trading risk management and decision-making. From common pitfalls like confirmation bias and overconfidence to the psychological impacts of loss aversion and herd mentality, we unpack the ways these biases can skew trading behavior and lead to poor outcomes. Learn how biases affect everything from stop-loss placement to risk-reward assessments, and discover effective strategies to mitigate their impact. With insights from DayTradingBusiness, you'll be equipped to recognize and address your own biases, helping you to trade smarter and more disciplined in the long run.
How Do Cognitive Biases Influence Trading Decisions?
Cognitive biases distort traders’ perception of risk, leading to overconfidence, impulsive decisions, or neglect of warning signs. For example, confirmation bias makes traders ignore conflicting data, increasing exposure to losses. Anchoring bias causes sticking to initial price targets despite new information, skewing risk assessment. Overconfidence leads to excessive trading and underestimated risks. These biases cause traders to misjudge market volatility, ignore diversification, and take unnecessary risks, undermining effective risk management.
What Are Common Cognitive Biases in Trading?
Common cognitive biases in trading include overconfidence, confirmation bias, loss aversion, herd mentality, and recency bias. These biases lead traders to underestimate risks, cling to losing positions, follow the crowd without analysis, and focus too much on recent events, impairing effective risk management.
How Does Confirmation Bias Impact Trading Risk?
Confirmation bias causes traders to focus only on information that supports their existing views, ignoring warning signs. This leads to holding onto losing positions too long or overestimating chances of success, increasing trading risk. It skews risk assessment, making traders underestimate potential losses and overestimate gains. As a result, they take bigger risks based on selective info, risking more capital than they should.
Can Overconfidence Lead to Poor Trading Outcomes?
Yes, overconfidence can lead to poor trading outcomes by causing traders to underestimate risks, overtrade, and ignore warning signs. It skews risk management, making traders take bigger positions or hold onto losing trades longer, increasing losses. Overconfidence inflates perceived skill, leading to reckless decisions that can wipe out profits.
How Does Loss Aversion Affect Trading Behavior?
Loss aversion makes traders fear losses more than they value gains, leading to overly cautious or risky decisions. They might hold onto losing stocks too long, hoping to break even, or sell winners too early to lock in gains. It causes emotional reactions that skew risk management, often prompting impulsive trades or avoiding necessary risks. This bias can result in poor portfolio adjustments and increased vulnerability to market swings.
What Is the Role of Anchoring Bias in Trading?
Anchoring bias makes traders fixate on initial information, like a stock’s past price, leading them to underestimate future risks or overvalue certain assets. It causes traders to stick to initial impressions even when new data suggests a different direction, increasing chances of poor decision-making. In risk management, anchoring bias can prevent traders from adjusting their strategies promptly, risking bigger losses if they cling to outdated assumptions.
How Does Herd Mentality Influence Market Risks?
Herd mentality amplifies market risks by causing traders to follow the crowd without analyzing fundamentals, leading to bubbles and crashes. When investors mimic others’ decisions, it inflates asset prices beyond true value, increasing the risk of sudden corrections. This collective behavior fuels volatility, making markets unpredictable and risking significant losses if the herd suddenly turns. It undermines individual risk management, as traders ignore personal analysis and rely on prevailing trends, often resulting in poor timing and increased exposure to market swings.
How Can Cognitive Biases Cause Overtrading?
Cognitive biases like overconfidence, herd mentality, and confirmation bias make traders underestimate risks and overtrade. Overconfidence leads traders to believe they’re unbeatable, prompting excessive trades. Herd mentality causes traders to follow popular trends without proper analysis, increasing trading frequency. Confirmation bias makes traders ignore warning signs, sticking to flawed strategies and trading too often. These biases distort risk perception, pushing traders to take unnecessary risks and trade more than they should.
What Are the Risks of Emotional Trading Biases?
Emotional trading biases can cause impulsive decisions, leading to significant losses. They distort risk perception, making traders overconfident or fearful at the wrong moments. Biases like greed and fear trigger poor timing—buying high or selling low. They also cause traders to ignore data and stick to losing positions or abandon profitable ones. Over time, these biases undermine disciplined risk management, increasing the chance of substantial financial damage.
How Do Cognitive Biases Affect Stop-Loss Placement?
Cognitive biases like overconfidence, loss aversion, and herd behavior distort traders’ judgment, leading to poorly timed or inconsistent stop-loss placement. Overconfidence makes traders underestimate risks, causing them to set wider stops or avoid stops altogether. Loss aversion prompts traders to move stops closer to avoid realizing losses, increasing the chance of being stopped out prematurely. Herd behavior pushes traders to mimic others’ stop-loss levels, ignoring their own risk tolerance. These biases result in inconsistent risk management and can cause larger losses or missed profit opportunities.
Can Biases Lead to Ignoring Market Data?
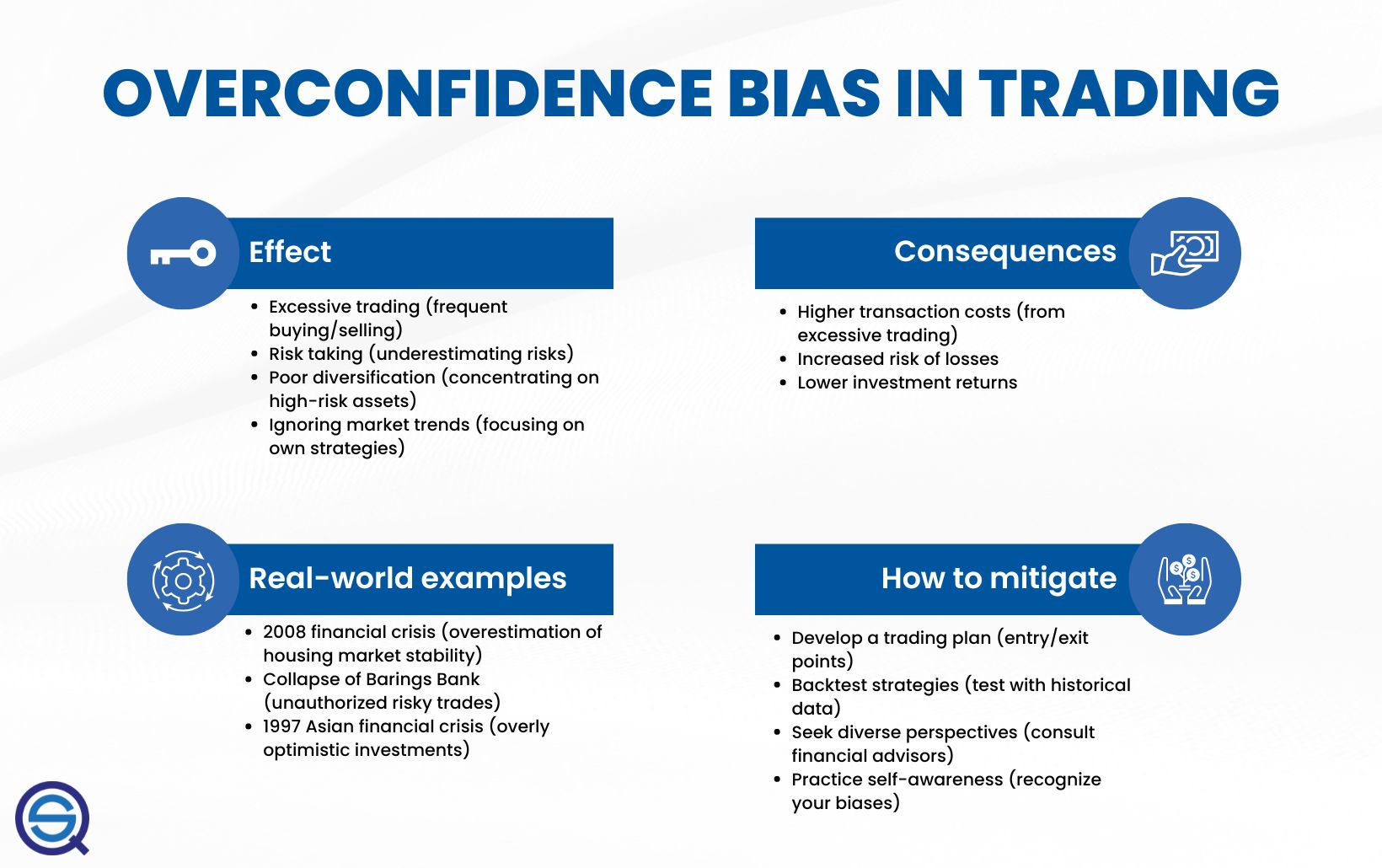
Yes, biases like confirmation bias or overconfidence can cause traders to ignore or dismiss market data that contradicts their views, leading to poor risk management.
How Do Cognitive Biases Impact Risk-Reward Assessment?
Cognitive biases distort traders' risk-reward assessments by clouding judgment. They cause overconfidence, leading traders to underestimate risks and chase bigger rewards. Confirmation bias makes traders ignore warning signs, skewing risk perception. Loss aversion makes traders hold onto losing positions, risking larger losses. Anchoring bias locks traders into initial estimates, skewing reward expectations. Overall, these biases lead to poor decision-making, increasing the likelihood of risky trades and misjudged rewards.
What Strategies Help Mitigate Cognitive Biases?
Using data-driven decisions, seeking diverse opinions, and implementing checklists help counteract cognitive biases in trading. Practicing mindfulness and maintaining emotional discipline prevent biases like overconfidence and loss aversion from skewing risk management. Setting predefined trading rules and using automation reduce impulsive decisions influenced by biases. Regularly reviewing trades and challenging assumptions keeps biases in check.
How Does Cognitive Bias Affect Trading Discipline?
Cognitive bias leads traders to misjudge risks, overconfidence, and emotional reactions, causing poor risk management. Biases like overconfidence inflate their perceived accuracy, making them take bigger positions without proper sizing. Confirmation bias makes traders ignore warning signs, sticking to losing trades. Loss aversion prompts holding onto bad trades longer, increasing risk. These biases distort judgment, undermining disciplined risk controls.
How Can Traders Recognize Their Own Biases?
Traders recognize their biases by reflecting on past decisions, questioning their motivations, and noting emotional triggers. Keeping a trading journal helps identify patterns like overconfidence or loss aversion. Seeking feedback from peers or mentors can reveal unconscious biases. Being aware of common biases—like confirmation bias or herd mentality—and monitoring emotional reactions during trades also aids recognition. Regularly reviewing trades objectively highlights biased patterns that influence risk management.
What Are the Long-Term Risks of Cognitive Biases in Trading?

Cognitive biases like overconfidence, loss aversion, and confirmation bias can cause traders to take bigger risks, ignore warning signs, and stick to losing strategies. Overconfidence leads to excessive trading and bigger positions, increasing potential losses. Loss aversion makes traders hold onto losing assets too long, risking bigger downturns. Confirmation bias causes ignoring data that contradicts beliefs, leading to poor decision-making. Over time, these biases erode discipline, inflate risk exposure, and cause consistent underperformance.
Conclusion about How Do Cognitive Biases Affect Trading Risk Management?
In conclusion, cognitive biases significantly influence trading risk management and decision-making. From confirmation bias to overconfidence, these psychological factors can lead to poor outcomes, including overtrading and ignoring critical market data. Understanding and recognizing these biases is essential for traders aiming to enhance their discipline and improve risk-reward assessments. Implementing strategies to mitigate these biases can lead to more informed decisions and better trading performance. For further insights and support in navigating these challenges, DayTradingBusiness provides valuable resources tailored to traders seeking to refine their approach.
Learn about How does stop-loss risk affect day trading profits?