Did you know that hedging in trading is like wearing a parachute while skydiving—it's not about avoiding the jump but ensuring a safer landing? In this article, we delve into the ins and outs of hedging in day trading, exploring its definition, protective benefits, and key advantages. We’ll highlight the risks associated with various hedging strategies, how they impact potential profits, and when they might be advisable for traders. Additionally, we’ll cover common techniques, the influence of market volatility, and whether hedging is suitable for beginners. Lastly, we’ll discuss the tools needed for effective hedging and alternatives for managing risk. Let DayTradingBusiness guide you through the complexities of hedging to enhance your trading strategy.
What is hedging in day trading?
Hedging in day trading is using strategies like options or inverse ETFs to offset potential losses on a primary position. It aims to protect your portfolio from sudden market swings. The main advantage is risk reduction during volatile moves, helping preserve capital. However, it can limit gains if the market moves favorably, and hedging costs—like premiums or fees—can eat into profits. It also adds complexity, requiring careful timing and understanding.
How does hedging protect day traders from losses?
Hedging protects day traders from losses by offsetting potential declines in their main positions with opposite trades, reducing overall risk. For example, if a trader owns a stock expecting it might drop, they can buy put options to limit potential losses. This strategy acts like insurance, cushioning the impact of sudden market moves.
What are the main advantages of hedging in day trading?
Hedging in day trading limits potential losses by offsetting positions, providing risk protection during volatile moves. It allows traders to stay in the market longer without fearing sudden adverse swings. Hedging can also help lock in profits or minimize damage when market conditions shift unexpectedly.
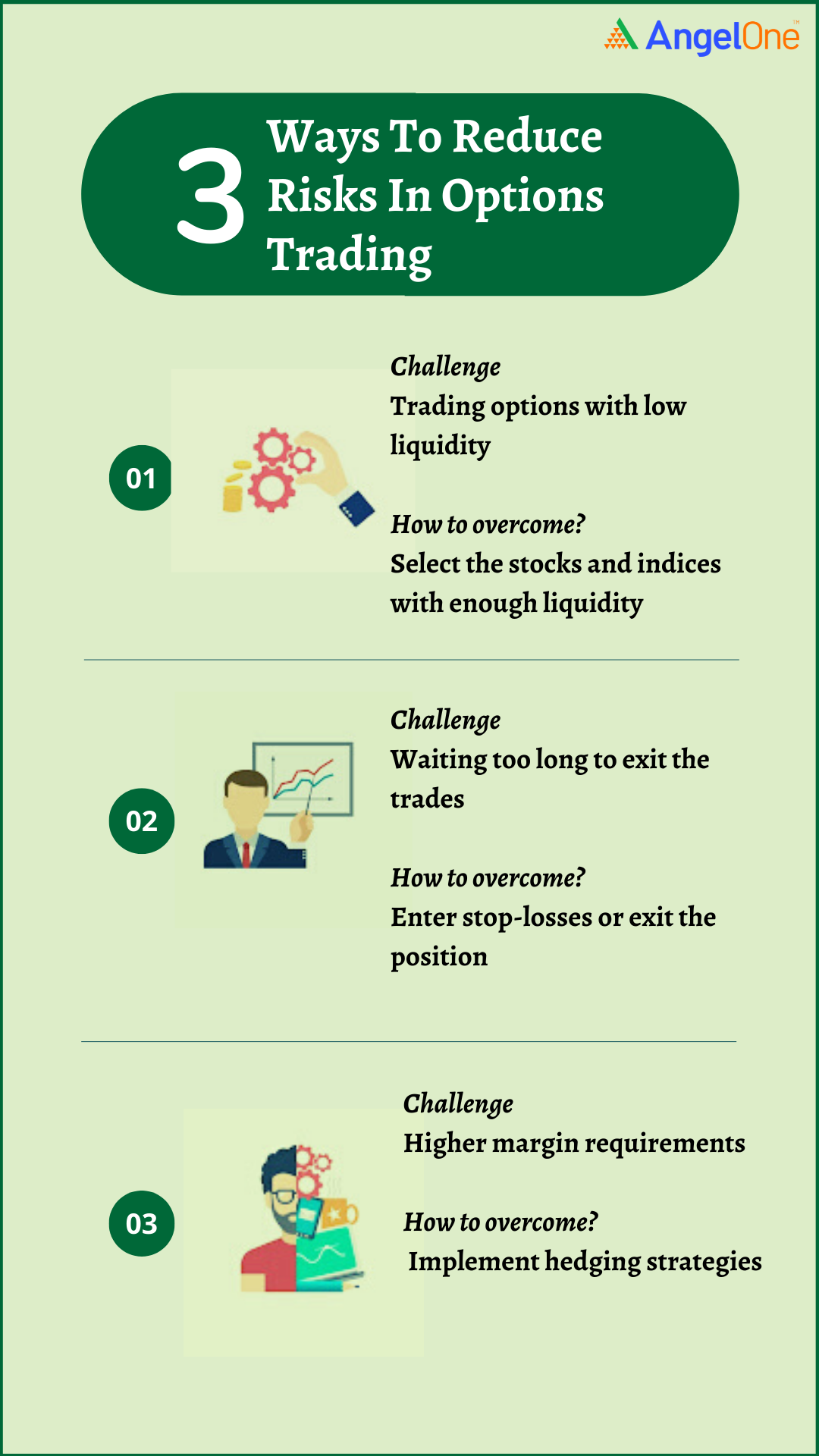
What risks are associated with hedging strategies?
Hedging in day trading can limit losses but also caps potential gains, adds complexity, and incurs transaction costs. It may lead to over-hedging, reducing profit margins. Incorrect hedging strategies can increase exposure if markets move unexpectedly. Additionally, frequent adjustments can cause slippage and higher fees, and small price movements might not justify the costs.
How does hedging affect potential profits in day trading?
Hedging limits potential profits by reducing risk, as gains on the primary position may be offset by losses on the hedge. It safeguards against big losses but can cap upside if the market moves favorably. In day trading, hedging can prevent large swings, but it also means missing out on full profit potential during strong trends.
When should a day trader consider using hedging?
A day trader should consider using hedging when risking significant losses on a position and wanting to protect gains or limit downside during high volatility. Hedge when market conditions are unpredictable or news events could cause sharp price swings. Use hedging to lock in profits or prevent losses if a trade moves against you quickly. Avoid hedging if it complicates your strategy or reduces potential gains during stable markets.
What are common hedging techniques for day traders?
Common hedging techniques for day traders include using options like puts and calls to protect against price swings, opening opposite positions in correlated assets, and employing futures contracts. Some traders also use stop-loss orders and diversify their trades to reduce risk.
How does hedging impact trading costs and fees?

Hedging increases trading costs and fees because it requires opening additional positions, leading to higher transaction expenses and spreads. It can double or triple trading fees as you execute more trades to protect your main position. This added cost can eat into profits or deepen losses if the hedge isn’t perfectly effective.
Can hedging prevent all types of trading losses?
No, hedging can't prevent all trading losses. It reduces risk but can't eliminate market volatility or sudden price swings that cause losses.
What are the disadvantages of using hedging in day trading?
Hedging in day trading limits potential gains because it often involves taking offsetting positions, reducing overall profit if the market moves favorably. It can be complex and requires extra capital, increasing transaction costs and tying up funds that could be used elsewhere. Hedging also adds to decision-making stress, as traders must manage multiple positions simultaneously, which can lead to mistakes or missed opportunities.
How does hedging influence trading psychology?
Hedging can reduce emotional stress by limiting potential losses, helping traders stay calmer during volatile markets. It provides a sense of security, making it easier to stick to a trading plan without panic. However, reliance on hedging might lead to overconfidence or complacency, causing traders to take bigger risks. If not managed well, it can also create confusion or indecision, as traders juggle multiple positions. Overall, hedging influences trading psychology by balancing risk awareness with emotional stability, but it requires discipline to avoid negative mental habits.
Is hedging suitable for beginner day traders?
Hedging can be risky for beginner day traders because it requires advanced understanding of markets, quick decision-making, and experience. It might protect against losses, but it also adds complexity and potential for bigger mistakes if not handled properly. For beginners, focusing on simple, straightforward trading strategies is usually better before trying to hedge.
Learn about Is hedging suitable for beginner day traders?
What are the best tools and platforms for hedging?
The best tools and platforms for hedging include Interactive Brokers, Thinkorswim by TD Ameritrade, and MetaTrader 5. They offer options, futures, and forex trading features essential for effective hedging. These platforms provide real-time data, advanced order types, and risk management tools, making it easier to implement hedging strategies.
How does market volatility affect hedging effectiveness?
Market volatility reduces hedging effectiveness because sudden price swings can cause hedges to lose value quickly, making risk management harder. When markets are turbulent, hedges may not offset losses as intended, leading to gaps and unexpected exposure. High volatility increases the cost of maintaining hedges due to frequent adjustments and wider spreads. Conversely, in stable markets, hedges work more predictably, protecting traders from downside risk.
What are the alternatives to hedging for risk management?

Alternatives to hedging for risk management include setting stop-loss orders, diversifying your trades across different assets, using position sizing to limit exposure, and employing options strategies like spreads.
Stop-loss orders automatically exit trades at a predetermined price, limiting losses.
Diversification spreads risk across multiple assets, reducing the impact of a single adverse move.
Adjusting position sizes keeps potential losses within acceptable limits.
Options strategies can protect against downside while maintaining upside potential.
Conclusion about What are the pros and cons of hedging in day trading?
In summary, while hedging can be a valuable strategy for day traders seeking to mitigate risks and protect profits, it comes with its own set of challenges and costs. Understanding the advantages, disadvantages, and effective techniques is crucial for optimizing your trading approach. For those looking to deepen their knowledge and refine their strategies, DayTradingBusiness offers essential insights and support tailored to your trading journey.