Did you know that the IRS once mistook a trader's frequent coffee runs for a tax loophole? While we can't guarantee a caffeine-fueled financial windfall, understanding the tax implications of forex and crypto day trading can help you navigate the complexities of profit and loss. In this article, we’ll explore special tax rules for forex and crypto trading, covering critical topics such as specific tax rates, reporting requirements, and the impact of losses. We’ll also delve into how to calculate taxes on crypto trades, the necessity of maintaining detailed records, and the potential advantages of short-term trading. With insights from DayTradingBusiness, you’ll learn how to manage your tax obligations effectively and possibly minimize your tax burden.
Are There Specific Tax Rules for Forex Trading?
Yes, forex trading has specific tax rules, including reporting gains and losses on IRS Form 8949 and Schedule D, with the potential for Section 1256 treatment, which taxes 60% of gains as long-term and 40% as short-term. Crypto day trading is taxed as property, requiring detailed records of each transaction, and profits are taxed as capital gains or ordinary income depending on the activity. Both have unique rules for reporting, and traders often need to use specific forms and follow particular IRS guidelines.
How Are Crypto Day Trades Taxed?
Crypto day trades are taxed as capital gains. Short-term trades held under a year are taxed at your ordinary income rate. If you hold crypto longer than a year, it qualifies for lower long-term capital gains tax. No special tax rules apply specifically to crypto day trading; it follows standard capital gains regulations. You must track each trade’s buy and sell prices for accurate reporting.
Do Forex and Crypto Trading Have Different Tax Rates?
Yes, forex and crypto trading often have different tax rules and rates. Forex trading may be taxed as ordinary income or capital gains, depending on the country, with specific rules for currency exchange gains. Crypto trading is typically taxed as property or capital gains, with rates varying based on holding periods and local regulations. Each asset class has distinct reporting requirements and tax treatments.
What Are the Reporting Requirements for Forex Gains?
Forex gains must be reported as ordinary income or capital gains, depending on activity. If trading as a business, report profits on Schedule C; if investing, use Schedule D. Keep detailed records of all trades, including dates, amounts, and currencies. Some countries require specific forms or disclosures for forex transactions. Crypto day trading may have similar rules but also often involves reporting crypto-specific transactions. Consult local tax laws for precise reporting requirements.
How Do I Calculate Taxes on Crypto Day Trades?
Crypto day trading taxes are calculated by tracking your gains and losses from each trade. You need to record the date, amount, and value at purchase and sale. When you sell crypto, the difference between the sale price and your cost basis is your taxable gain or deductible loss. Short-term gains from holding less than a year are taxed at your ordinary income rate. Use a crypto tax software or spreadsheets to stay organized. No special tax rules apply solely to crypto day trading; it’s taxed like other capital assets.
Are There Tax Advantages for Short-Term Trading?
Yes, short-term trading of forex and crypto can have tax advantages, like qualifying for trader tax status, which allows deducting related expenses directly. However, gains are typically taxed as ordinary income or short-term capital gains, leading to higher rates. Some traders use specific accounting methods, like mark-to-market, to treat gains and losses more favorably. Always check local laws, as tax rules for forex and crypto day trading vary by jurisdiction.
Can I Deduct Losses from Forex or Crypto Trading?
Yes, you can deduct losses from forex and crypto trading, but the rules vary. Forex trading losses may be deducted against gains if you file as a trader or use Section 988 or 1256 contracts. Crypto trading losses are treated as capital losses, deductible up to $3,000 annually against other income. Keep detailed records to substantiate losses and understand whether your trading qualifies for special tax treatment.
Do I Need to Keep Detailed Records of My Trades?

Yes, keeping detailed records of your trades is essential for accurate tax reporting and compliance, especially for forex and crypto day trading.
Are There Special Tax Forms for Forex or Crypto Income?
Yes, forex and crypto income have specific tax forms. Forex traders report income on IRS Form 6781 (Section 1256 contracts), which uses the 60/40 rule for gains and losses. Crypto traders typically report on Schedule D and Form 8949, but some transactions, like staking or mining, may require additional forms. The IRS treats crypto as property, so each transaction might need detailed reporting.
How Does Wash Sale Rule Apply to Crypto?
The wash sale rule doesn’t currently apply to crypto because the IRS treats cryptocurrencies as property, not securities. Therefore, losses from crypto trades can't be disallowed if you buy back the same crypto within 30 days. For forex day trading, the wash sale rule generally doesn’t apply either, since forex is considered a different asset class. However, tax rules for crypto and forex trading can change, so stay updated.
Are Crypto Staking and Lending Considered taxable?
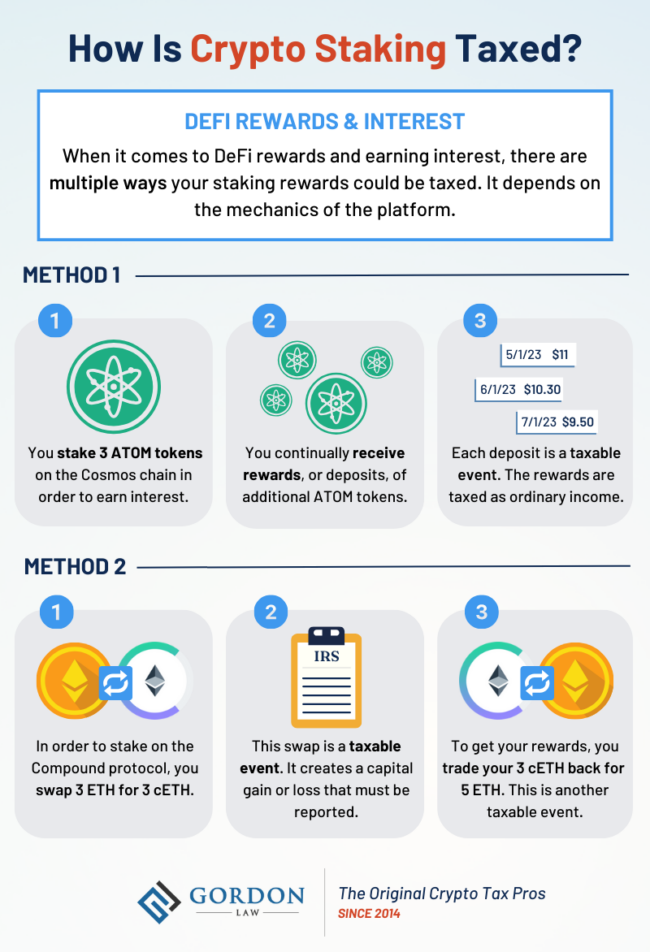
Yes, crypto staking and lending are taxable events. Staking rewards and interest earned from lending are considered taxable income.
What Are the Tax Implications of Margin Trading?
Margin trading profits are taxable as capital gains or ordinary income, depending on your trading activity and jurisdiction. You must report gains and losses on your tax return, and margin interest may be deductible. For forex trading, specific IRS rules treat gains as Section 1256 contracts or forex contracts, with different tax rates. Crypto day trading profits are generally taxed as property, meaning gains are realized when you sell or exchange crypto. Keep detailed records of all trades, including margin interest and crypto transactions, to accurately report taxes.
How Do I Handle Tax When Switching Between Forex and Crypto?

When switching between forex and crypto day trading, track each trade's gains and losses separately. Report forex profits under Section 988 or Section 1256, depending on your jurisdiction, and crypto gains as property, using Schedule D or relevant forms. Maintain detailed records of all transactions, including dates, amounts, and prices. Be aware that crypto may require reporting on Form 8949, while forex might have specific tax treatments. Consult a tax professional to ensure proper classification and compliance.
Are There Different Tax Rules for Automated Trading Bots?
Yes, forex and crypto day trading have specific tax rules. Crypto profits are usually taxed as capital gains, with short-term gains taxed as ordinary income. Forex trading often follows special rules, like Section 1256 contracts, which have a 60/40 split between long-term and short-term capital gains. Different regulations apply depending on the asset and trading frequency.
How Can I Minimize Taxes on Forex and Crypto Day Trading?
Yes, there are specific tax rules for forex and crypto day trading. Forex trading often qualifies for Section 1256 contracts, which are taxed at 60% long-term and 40% short-term capital gains, regardless of holding period. Crypto trading is taxed as property; every trade is a taxable event, and you must report gains and losses. To minimize taxes, use tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs for crypto, offset gains with losses, and keep detailed records of all trades. Consider holding assets longer to benefit from lower long-term capital gains rates, and consult a tax professional familiar with forex and crypto regulations.
Learn about How to minimize leverage risk in day trading?
Conclusion about Are There Special Tax Rules for Forex or Crypto Day Trading?
Understanding the tax implications of Forex and crypto day trading is crucial for maximizing your profits and ensuring compliance. Specific rules apply to each trading type, from reporting requirements to potential deductions for losses. By maintaining detailed records and being aware of the unique regulations, traders can navigate the complexities of taxation effectively. For tailored guidance and expert insights on managing your trading taxes, DayTradingBusiness offers comprehensive resources to help you stay informed and optimize your strategy.