Did you know that the average person forgets about 90% of their dreams? Well, when it comes to record-keeping in trading, forgetting is not an option. This article dives deep into the record-keeping requirements set forth by the SEC and FINRA, essential for financial firms and broker-dealers. You'll learn about the specific records required, retention timelines, and the critical differences between SEC and FINRA regulations. Additionally, we cover best practices for secure storage, handling client communications, and what happens if firms fail to comply. With recent updates in mind, this guide equips you with the knowledge to navigate record-keeping obligations effectively—because at DayTradingBusiness, we believe that informed trading is successful trading.
What are SEC record-keeping requirements for financial firms?
Financial firms must keep detailed records of all transactions, communications, and client accounts for at least five years, with the first two years in an easily accessible location. They’re required to maintain copies of emails, trade logs, account statements, and supervisory documentation. Firms must preserve records in a format that’s retrievable and readable, including electronic records. They also need to retain supervision and compliance records for specific periods, typically three to six years, depending on the document type. These rules ensure transparency, accountability, and regulatory oversight by the SEC and FINRA.
How long must firms retain SEC records?
Firms must retain SEC records for at least five years.
What records are required by FINRA for broker-dealers?
FINRA requires broker-dealers to keep records of all written communications related to their business, including emails and instant messages, for at least three years. They must maintain a detailed books-and-records system, including customer account records, trade tickets, and financial statements, for six years. Additionally, firms need to preserve order tickets, blotters, and correspondence to ensure compliance and regulatory review.
Are electronic records covered under SEC and FINRA rules?
Yes, electronic records are covered under SEC and FINRA rules. Both agencies require firms to maintain electronic communications, trading records, and other digital documents in a format that allows easy retrieval and review. They specify that electronic storage must be reliable, tamper-evident, and accessible for regulatory examinations.
What are the specific record-keeping rules for securities transactions?
Securities transactions must be recorded promptly and accurately, including details like trade date, settlement date, security name, quantity, price, and parties involved. Firms are required to keep records of order tickets, trade confirmations, and account statements for at least six years. Electronic records should be stored securely, with backups, and remain accessible for audit. Any modifications or corrections must be clearly documented with dates and reasons. These rules ensure transparency, compliance, and proper supervision.
How do SEC rules differ from FINRA on record retention?
SEC rules require broker-dealers to retain books and records for at least six years, with the first two years in an accessible location. FINRA mandates firms keep records for six years as well but emphasizes more detailed categories, like electronic communications, requiring retention of all forms of communication related to business. SEC focuses on broad record types and retention periods, while FINRA specifies detailed procedures and record categories, often demanding more comprehensive documentation and electronic record-keeping.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with record-keeping rules?
Penalties for not following SEC and FINRA record-keeping rules include fines, suspension, or banning from the industry. Firms can face regulatory enforcement actions, increased audits, and reputational damage. Individuals may be subject to disciplinary actions, including license suspension or revocation. Non-compliance can also lead to legal liabilities if records are used as evidence in investigations or lawsuits.
What documents must be preserved under SEC regulations?

Under SEC regulations, companies must preserve financial records, audit reports, internal communications, and correspondence related to securities transactions for at least five years. They must also keep records of insider trades, shareholder records, and filings like Form 10-K and 10-Q for the same period. FINRA requires firms to retain communications, transaction records, and customer account information for six years. Both regulators demand preserving documents that support compliance, transparency, and accurate reporting in securities activities.
How do firms handle client communications under these rules?
Firms log all client interactions, email, and phone calls, maintaining detailed, accurate records. They use secure systems to store communications, ensuring easy retrieval for audits or disputes. Regular training emphasizes compliance with SEC and FINRA record-keeping rules. They document advice given, client instructions, and correspondence promptly. This transparency helps demonstrate adherence to regulatory standards and protects against violations.
What are the record-keeping timelines mandated by SEC and FINRA?
SEC requires firms to keep records related to securities transactions for at least three years, with the most critical records retained for six years. FINRA mandates that firms preserve books and records for a minimum of six years, including three years in an easily accessible location. Both regulators emphasize maintaining detailed, accurate records of communications, transactions, and supervisory documentation to ensure compliance and facilitate audits.
Are there special rules for record retention during audits?
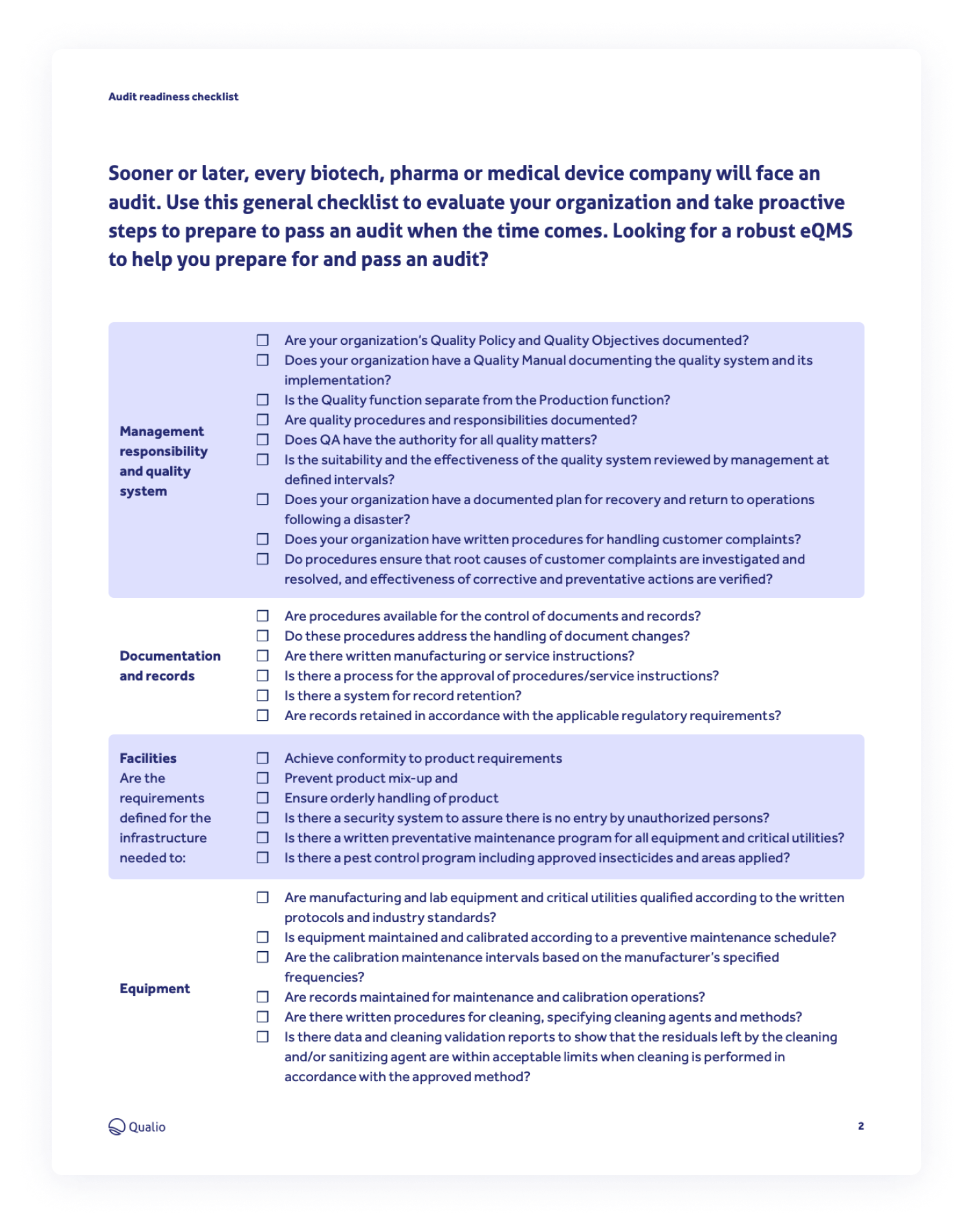
Yes, during audits, SEC and FINRA require firms to retain all relevant records, including communications, transaction records, and internal documents, for specified periods—typically five years for SEC and three to six years for FINRA. These records must be complete, accurate, and readily accessible. Firms should avoid deleting or altering records during an audit and ensure proper organization to facilitate easy review.
What are the best practices for secure record storage?
Store records securely using encrypted digital storage or locked cabinets. Limit access to authorized personnel only. Regularly back up data off-site. Maintain clear, organized records to prevent loss or tampering. Follow SEC and FINRA guidelines for retention periods and confidentiality. Use strong passwords and cybersecurity measures to protect electronic records. Conduct periodic audits to ensure compliance and security.
How do record-keeping rules apply to digital communications like emails?
Record-keeping rules require firms to retain digital communications, including emails, for a specified period—generally six years for SEC and FINRA. These rules mean emails related to business activities, client interactions, or transactions must be stored securely and easily accessible during audits or investigations. Firms must implement systems that capture, archive, and retrieve digital messages without alteration or loss. This ensures compliance with regulations and preserves a complete record of communications relevant to securities activities.
What are the requirements for archiving trade data?

To archive trade data according to SEC and FINRA rules, firms must securely store records of all trade transactions, communications, and related documents for at least six years. The data must be accurate, complete, and readily accessible for regulatory inspections. Electronic records should be backed up regularly and stored in a format that prevents alteration. Firms need to implement proper record-keeping systems, including audit trails, and ensure data integrity and confidentiality.
How do record-keeping rules impact compliance monitoring?
Record-keeping rules by SEC and FINRA ensure firms maintain accurate, complete, and accessible records, making compliance monitoring easier. They enable regulators to verify that firms follow laws, detect misconduct, and enforce penalties efficiently. Proper records help identify violations quickly, reducing risks of non-compliance and financial penalties. Without strict record-keeping, monitoring becomes guesswork, increasing the chance of missed issues and regulatory sanctions.
What are the recent updates to SEC and FINRA record-keeping rules?
Recent updates to SEC and FINRA record-keeping rules require firms to retain electronic communications, including social media and instant messages, for at least five years. The SEC emphasized the need for firms to implement robust electronic storage systems to ensure records are complete, searchable, and tamper-proof. FINRA now mandates more detailed supervisory procedures to monitor digital communications and enhance compliance. Both regulators focus on increasing transparency and ensuring firms preserve all relevant records in their original format for regulatory reviews.
How can firms ensure they meet all record-keeping obligations?
Firms can meet record-keeping obligations by implementing a comprehensive compliance system that follows SEC and FINRA rules, maintaining detailed, accurate, and retrievable records of all transactions and communications, regularly training staff on record retention requirements, and conducting internal audits to ensure adherence. Using automated record management software aligned with regulatory standards helps prevent violations. Staying updated on SEC and FINRA rule changes and consulting legal or compliance experts ensures ongoing compliance.
Conclusion about What Are the Record-Keeping Rules by SEC and FINRA?
In summary, understanding the record-keeping rules set forth by the SEC and FINRA is crucial for financial firms to ensure compliance and avoid penalties. Firms must meticulously retain various records, including electronic communications, for specified durations while adhering to distinct SEC and FINRA guidelines. Properly managing client communications and maintaining secure storage practices are essential for compliance monitoring and audit readiness. For comprehensive insights and support in navigating these complex regulations, consult with DayTradingBusiness to enhance your trading operations.