Did you know that using an automated trading system can sometimes feel like trying to teach a cat to fetch? It sounds great in theory, but the legal risks can be unpredictable. In this article, we delve into the legal implications of using automated trading systems, addressing critical questions such as the potential for violating securities laws and the regulations that govern these platforms. We’ll explore the legal responsibilities traders have, the risks of market manipulation, and what steps to take before deploying an automated system. With insights from DayTradingBusiness, you’ll be better equipped to navigate the legal landscape of algorithmic trading and ensure compliance, ultimately safeguarding your trading ventures.
What are the legal risks of using automated trading systems?
Using automated trading systems can lead to legal risks like violating securities laws if the system manipulates markets or creates false impressions. You might face lawsuits if your algorithm causes market disruptions or breaches insider trading regulations. Regulatory agencies can impose fines or bans if your system doesn't comply with trading rules or fails to disclose its use properly. There’s also liability if your system makes errors causing financial losses, especially if negligence or misrepresentation is involved. Overall, improper use or non-compliance with trading regulations can result in legal action, fines, or suspension of trading privileges.
Can automated trading violate securities laws?
Yes, automated trading can violate securities laws if it manipulates markets, involves insider trading, or breaches regulations like order execution rules. Using algorithms that intentionally manipulate prices or create false market activity is illegal. Traders must comply with regulations on fair trading practices and proper disclosure to avoid legal risks.
Is algorithmic trading legal in my country?
Check your country's financial regulations or consult a lawyer to confirm if algorithmic trading is legal where you are.
What regulations govern automated trading platforms?
Automated trading platforms are governed by securities laws, SEC or FCA regulations, and FINRA rules. They must comply with anti-fraud, transparency, and reporting requirements. Regulations also include registration obligations for operators and requirements for risk management and algorithm disclosure.
Are there penalties for non-compliance with trading laws?
Yes, there are penalties for non-compliance with trading laws, including fines, account suspension, legal actions, and potential criminal charges.
How does insider trading relate to automated trading?
Insider trading risks increase with automated trading systems because algorithms can execute trades based on non-public, material information if programmed improperly or hacked. Automated systems lack judgment, so if they access or act on insider info, it can lead to illegal trading. Regulators scrutinize automated trades closely, and any connection to insider trading can result in severe legal penalties. Using automated trading without strict compliance measures heightens the risk of unintentional insider trading violations.
Can automated trading lead to market manipulation charges?
Yes, automated trading can lead to market manipulation charges if it involves practices like spoofing, quote stuffing, or creating false market signals. Regulators monitor algorithms for manipulative behaviors, and violations can result in legal action.
What legal responsibilities do traders have when using bots?
Traders using bots must comply with securities laws and regulations, avoid market manipulation, and ensure their bots don’t execute fraudulent or deceptive trades. They’re responsible for the bot’s actions, monitoring for compliance, and preventing insider trading or manipulation. Failing to follow exchange rules or misusing bots can lead to fines, sanctions, or legal action.
Are there licensing requirements for automated trading software?
Yes, some jurisdictions require licensing or registration for automated trading software, especially if it involves managing client funds or providing trading signals. Regulations vary by country, and failure to comply can lead to legal penalties. Always check local securities laws before deploying automated trading systems.
How do regulators monitor automated trading activities?
Regulators monitor automated trading activities through real-time surveillance systems that track trading patterns, identify anomalies, and detect manipulative behaviors like spoofing or layering. They analyze order book data, trade executions, and algorithmic signals to spot suspicious activities. Regulators also require firms to report their algorithmic trading strategies and maintain audit trails for review. Automated alerts flag unusual trading spikes or rapid order placements, prompting investigations. Some regulators use advanced analytics and machine learning to spot emerging risks in high-frequency trading.
What are the risks of using unregulated trading algorithms?
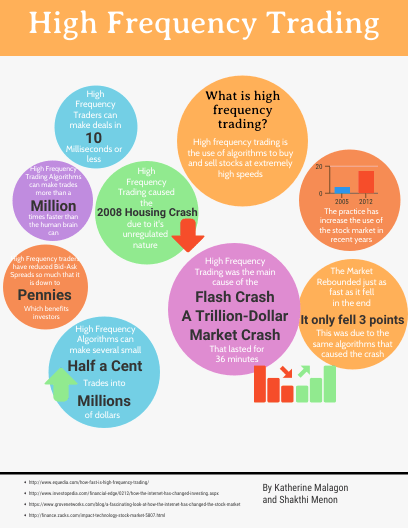
Using unregulated trading algorithms risks legal violations like market manipulation, insider trading, and breach of financial regulations. It can lead to fines, sanctions, or legal action if authorities find the algorithms violate trading laws. Unregulated systems may also cause unfair market practices, exposing users to lawsuits or penalties.
Can automated trading systems cause legal disputes?
Yes, automated trading systems can cause legal disputes, especially if they violate market regulations, manipulate prices, or breach trading laws. Errors in algorithms leading to significant financial losses can also trigger legal claims. Regulatory authorities may investigate if the system's activity breaches securities laws, resulting in legal conflicts.
How does risk of fraud impact automated trading?
The risk of fraud in automated trading can lead to legal actions if malicious actors manipulate algorithms or data. It increases the chance of financial losses and legal disputes, forcing traders to implement stricter compliance measures. Fraudulent schemes like spoofing or pump-and-dump can exploit automated systems, risking regulatory penalties. Overall, the threat of fraud makes automated trading riskier legally, requiring robust security and monitoring.
Learn about How does leverage impact stop-loss risk in day trading?
What legal steps should I take before deploying an automated system?
Review regulations on automated trading in your jurisdiction. Obtain necessary licenses or approvals. Draft clear terms of use and user agreements. Ensure compliance with securities laws and data privacy regulations. Conduct risk assessments and include disclaimers about system limitations. Consult a legal expert to address potential liability issues and ensure transparency.
How are disputes over automated trading resolved legally?
Disputes over automated trading are resolved through legal action in courts, often involving breach of contract, negligence, or violation of securities laws. Traders or firms may file lawsuits alleging system failures, algorithm errors, or misrepresentation. Regulatory agencies like the SEC can investigate and enforce penalties. Arbitration clauses in trading agreements often require disputes to be settled through arbitration instead of court. Legal resolution depends on contractual terms, the nature of the dispute, and applicable securities regulations.
Conclusion about Legal Risks Associated with Using Automated Trading Systems
In conclusion, navigating the legal landscape of automated trading systems requires careful consideration of regulations and compliance. Traders must remain vigilant about potential violations, penalties, and the responsibilities that come with using these technologies. To ensure a safe trading experience, it is essential to stay informed and seek guidance from trusted sources like DayTradingBusiness, which can provide valuable insights into the complexities of trading law and best practices.
Sources:
- An Exchange Is a Many-Splendored Thing: The Classification and ...
- From decision optimization to satisficing: Regulation of automated ...
- Stock Market Development in Sub-Saharan Africa: Critical Issues ...
- Book Review: Algo Bots and the Law | CFA Institute Enterprising ...
- Machines that make and keep promises - Lessons for contract ...
- An artificial intelligence algorithmic approach to ethical decision ...