Did you know that the infamous Ponzi scheme was named after Charles Ponzi, who managed to swindle investors out of millions by promising unrealistic returns? Just like Ponzi, day traders must navigate a complex landscape of anti-fraud laws to avoid falling into legal traps. This article provides a comprehensive overview of how these laws affect day trading, including the specific fraud rules that apply, potential penalties for violations, and the common types of fraud to watch for. Discover how anti-fraud measures protect investors, the role of the SEC and FINRA in regulation, and essential disclosures required for compliance. With insights from DayTradingBusiness, you'll learn how to steer clear of legal issues and understand the implications of misleading information in marketing.
How do anti-fraud laws affect day trading?
Anti-fraud laws require day traders to be honest and transparent in their trading activities. They prevent manipulation, false advertising, and deceptive practices that could mislead other traders. If a day trader commits fraud, they can face legal penalties, fines, and bans from trading platforms. These laws also enforce accurate disclosures about risks and profits, ensuring traders can't misrepresent their strategies or performance. Overall, anti-fraud laws create a safer trading environment by holding day traders accountable for dishonest practices.
What specific fraud rules apply to day traders?
Day traders must follow SEC and FINRA regulations, including rules against deceptive practices, misrepresentation, and market manipulation. They can't falsely inflate stock prices or spread false info to manipulate markets. They’re also subject to anti-fraud provisions like Rule 10b-5, which prohibits any scheme to defraud or deceive investors. Broker-dealers must verify customer identities under AML laws, and any suspicious activity must be reported. Violating these rules can lead to fines, account restrictions, or legal action.
Are there penalties for violating anti-fraud laws in day trading?
Yes, violating anti-fraud laws in day trading can lead to penalties like fines, account suspensions, and legal action, including criminal charges.
How do anti-fraud laws protect day trading investors?
Anti-fraud laws protect day trading investors by preventing manipulation, false statements, and deceptive practices. They ensure transparency in trading activities, making it illegal for anyone to mislead traders with false info or pump-and-dump schemes. Regulatory agencies like the SEC monitor and penalize fraudulent actions, helping investors avoid scams. These laws also require clear disclosure of risks and trading conditions, shielding day traders from deceptive tactics.
What types of fraud are common in day trading?
Common frauds in day trading include pump-and-dump schemes, where traders inflate stock prices to sell at a profit, and false or misleading information to manipulate stock prices. Insider trading, using non-public info to gain an advantage, also occurs. Additionally, broker fraud, like unauthorized trades or misrepresentation of account risks, is prevalent. Anti-fraud laws in day trading aim to prevent these, holding perpetrators accountable under SEC regulations and the Securities Act, ensuring transparency and fair market practices.
Do anti-fraud laws differ for retail vs. professional day traders?
Yes, anti-fraud laws differ for retail and professional day traders. Retail traders face regulations from the SEC and FINRA, focusing on protecting individual investors from misleading practices. Professional day traders, often classified as institutional or accredited investors, are subject to stricter compliance standards, but have more sophisticated legal protections. The core anti-fraud rules—like prohibiting false statements and manipulative tactics—apply to both, but enforcement and specific obligations vary based on trader status and whether they’re operating as individuals or institutions.
How can day traders avoid legal issues related to fraud?
Day traders can avoid legal issues by strictly following anti-fraud laws, such as accurately reporting trades, avoiding market manipulation, and not spreading false information. They should comply with SEC regulations, use transparent trading practices, and stay informed about insider trading and pump-and-dump laws. Keeping detailed records and avoiding deceptive tactics ensures they don’t violate anti-fraud statutes.
What disclosures are required under anti-fraud laws for day trading?
Day trading disclosures under anti-fraud laws require brokers to clearly explain risks, commissions, and potential conflicts of interest. They must disclose that day trading involves significant risks, including the possibility of substantial losses. Brokers also need to inform traders about the pattern day trader rule, margin requirements, and the volatile nature of the market. Any material misrepresentations or omissions about trading strategies, risks, or costs are illegal.
How does the SEC regulate fraud in day trading?
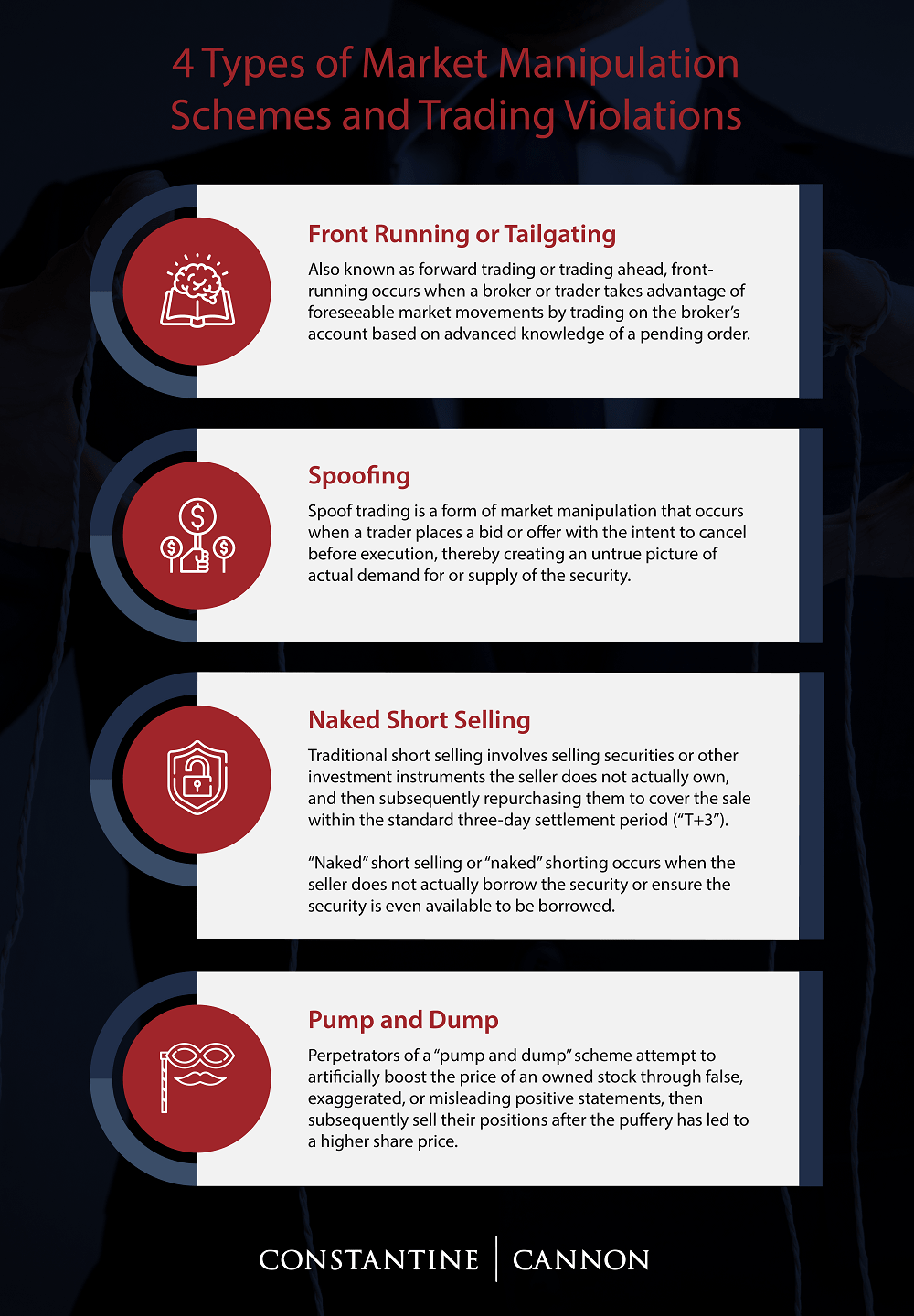
The SEC enforces anti-fraud laws by investigating false statements, pump-and-dump schemes, and manipulative practices in day trading. It monitors trading activity for insider trading and market manipulation, prosecuting violators to protect investors. The SEC requires transparency and honesty from brokers and traders, cracking down on deceptive tactics to prevent fraud in day trading.
What role does the FINRA play in preventing fraud among day traders?
FINRA enforces rules that require day traders to follow strict disclosure and trading practices, monitoring for suspicious activity. It investigates fraud, manipulative schemes, and deceptive practices in day trading, imposing fines or bans. FINRA's oversight ensures traders adhere to regulations designed to prevent scams like pump-and-dump schemes or false advertising. Its role is to catch and stop fraudulent behavior before it harms investors.
Are there legal risks for using misleading information in day trading?
Yes, using misleading information in day trading can lead to legal risks under anti-fraud laws. Regulators like the SEC can pursue enforcement actions if false statements manipulate markets or deceive investors. Violating these laws can result in fines, civil penalties, or criminal charges.
Learn about Are There Legal Limits on Leverage in Day Trading?
How do anti-fraud laws apply to algorithmic or high-frequency trading?
Anti-fraud laws prohibit deception, manipulation, and false statements in day trading, including algorithmic and high-frequency trading. Traders using algorithms must avoid manipulative practices like spoofing or quote stuffing, which are illegal under anti-fraud statutes. Regulators scrutinize algorithmic trading for signs of market manipulation, and violations can lead to fines or criminal charges. The laws aim to ensure fair markets, so any algorithmic strategy that misleads or distorts prices breaches anti-fraud regulations.
What are the consequences of fraudulent activity in day trading?
Fraudulent activity in day trading can lead to severe consequences like hefty fines, account bans, and criminal charges. Traders caught manipulating markets or providing false information face legal action from authorities like the SEC. These anti-fraud laws aim to protect market integrity, and violations can result in jail time, damage to reputation, and loss of trading privileges.
Can day traders be sued for fraud under anti-fraud laws?
Yes, day traders can be sued for fraud under anti-fraud laws if they intentionally mislead or deceive investors—for example, through false statements, market manipulation, or insider trading. Anti-fraud laws like the Securities Exchange Act prohibit such misconduct, and authorities or investors can pursue legal action against traders who violate these rules.
How do anti-fraud laws impact marketing and promotions in day trading?
Anti-fraud laws restrict false advertising, misleading claims, and deceptive practices in day trading promotions. They require clear, truthful information about risks and returns, preventing promoters from exaggerating potential gains. Violating these laws can lead to fines, legal actions, and damage to reputation. Marketing strategies must prioritize transparency to comply with anti-fraud regulations in day trading.
Learn about How Do Securities Laws Impact Day Traders?
Conclusion about How do anti-fraud laws apply to day trading?

In summary, understanding anti-fraud laws is crucial for anyone involved in day trading. These regulations not only safeguard investors but also delineate the boundaries of acceptable trading practices. Day traders must be aware of specific fraud rules, potential penalties, and necessary disclosures to mitigate legal risks. Staying informed about SEC and FINRA regulations can further enhance compliance and protect against fraudulent activities. By adhering to these guidelines, traders can navigate the market responsibly and ethically, ensuring a more secure trading environment. For detailed insights and support, DayTradingBusiness is here to help you navigate these complexities.
Sources:
- Financial Fraud: A Review of Anomaly Detection Techniques and ...
- The role of artificial intelligence in preventing corporate crime ...
- Using Virtual Bids to Manipulate the Value of Financial Transmission ...
- Securities Regulation and Administrative Law in the Roberts Court
- Speech, Greenspan -- Government regulation and derivative ... - FRB
- Suspicious trading in nonfungible tokens (NFTs) - ScienceDirect