Did you know that the stock market can be as unpredictable as a cat on a hot tin roof? Understanding volatility is crucial for day traders, especially when dealing with options. This article dives deep into the impact of volatility on day trading options, covering essential topics like what volatility means in this context, how it influences option pricing, and the significance of implied volatility. We’ll explore strategies for navigating high volatility, measuring volatility effectively, and the role of historical volatility in trading decisions. You'll also learn about common volatility indicators, how to profit from market fluctuations, and ways to manage risks effectively. Join DayTradingBusiness as we unpack these vital concepts and equip you with the knowledge to thrive in volatile markets.
What is volatility in day trading options?
Volatility in day trading options refers to the degree of price fluctuations of an underlying asset over a specific period. Higher volatility means larger price swings, which can create more opportunities and risks for traders. Options with high implied volatility typically have higher premiums, making them more expensive to buy. Traders often use volatility to gauge potential price movements and to strategize their trades, aiming to capitalize on rapid changes in the market. Understanding volatility is crucial for managing risk and maximizing profit in day trading options.
How does volatility affect option pricing?
Volatility significantly affects option pricing by influencing the premium. Higher volatility increases the expected price swings of the underlying asset, leading to higher option premiums. This is because greater uncertainty raises the potential for the option to end up in-the-money. Conversely, lower volatility results in lower premiums, as there’s less expected movement in the asset's price. For day trading options, understanding volatility helps traders anticipate price changes and make informed decisions on buying or selling options.
Why is implied volatility important for day traders?
Implied volatility is crucial for day traders because it indicates market expectations for future price movements. Higher implied volatility often leads to larger price swings, presenting more opportunities for profit. It also affects options pricing; when implied volatility rises, option premiums increase, allowing traders to capitalize on price movements effectively. Understanding implied volatility helps traders assess risk and make informed decisions, enhancing their strategies in a fast-paced trading environment.
What are the best strategies for trading options during high volatility?
The best strategies for trading options during high volatility include:
1. Straddles and Strangles: Buy both call and put options to profit from significant price movements in either direction.
2. Iron Condors: Sell out-of-the-money call and put spreads to capitalize on high premium collection when expecting less movement.
3. Calendar Spreads: Buy longer-term options and sell short-term options to benefit from time decay, especially when anticipating volatility spikes.
4. Directional Trades: Use options to leverage positions on stocks expected to move sharply, focusing on buying calls or puts based on market sentiment.
5. Volatility Index Options: Trade options on volatility indexes like VIX to hedge against risk or speculate on volatility changes.
6. Position Sizing: Adjust the size of your trades to manage risk effectively, as high volatility can lead to increased price swings.
7. Technical Analysis: Utilize charts and indicators to identify entry and exit points that align with volatility patterns, enhancing your timing.
These strategies can help maximize profits and manage risks effectively in a volatile market.
How can I measure volatility when trading options?
To measure volatility when trading options, use the following methods:
1. Implied Volatility (IV): Check the IV of the option, which reflects market expectations of future volatility. Higher IV usually indicates greater expected price swings.
2. Historical Volatility (HV): Analyze past price movements of the underlying asset. Calculate HV using standard deviation over a specific period to understand how much the price has fluctuated in the past.
3. VIX Index: Monitor the VIX, known as the "fear gauge." It represents market expectations of near-term volatility for the S&P 500 and can signal broader market sentiment.
4. Option Greeks: Pay attention to the Vega Greek, which measures how much an option's price changes with a 1% change in IV. This helps assess sensitivity to volatility.
5. Price Charts: Use technical analysis on price charts to identify patterns and volatility indicators, such as Bollinger Bands, which can show price range and volatility expansion or contraction.
By combining these methods, you can effectively gauge volatility and make informed decisions in your options trading strategy.
What role does historical volatility play in option trading?
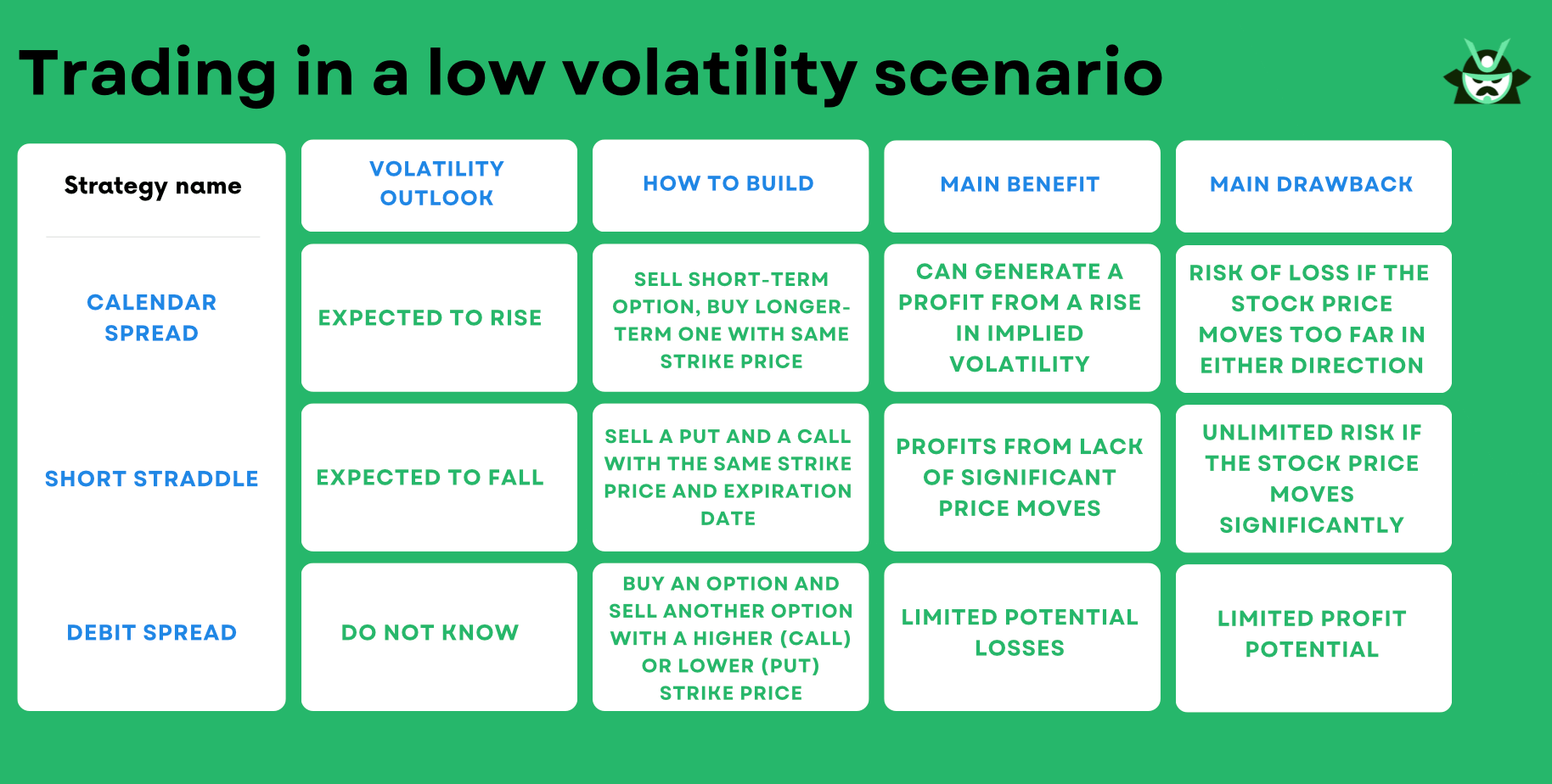
Historical volatility measures how much an asset's price has fluctuated over a specific period. In option trading, it helps traders assess the likelihood of price movements, influencing decisions on option pricing and strategy. High historical volatility suggests larger price swings, making options more expensive and potentially more profitable. Conversely, low volatility indicates stability, leading to cheaper options but possibly lower returns. Understanding historical volatility allows traders to anticipate market behavior and adjust their strategies accordingly, enhancing their chances of success in day trading options.
How does market volatility impact day trading decisions?
Market volatility significantly influences day trading decisions by affecting price movement and risk assessment. Higher volatility often leads to larger price swings, which can create more opportunities for profit. Traders typically look for volatile stocks to capitalize on rapid changes. However, increased volatility also raises the risk of substantial losses, prompting traders to implement tighter stop-loss orders and risk management strategies. Ultimately, day traders often adjust their entry and exit points based on current volatility levels to maximize gains while minimizing risk.
What are the common volatility indicators for options trading?
Common volatility indicators for options trading include:
1. Implied Volatility (IV) – Reflects the market's forecast of a stock's volatility based on option prices.
2. Historical Volatility (HV) – Measures past price fluctuations over a specific period.
3. VIX (Volatility Index) – Indicates market expectations of near-term volatility, often referred to as the "fear gauge."
4. Average True Range (ATR) – Assesses market volatility by measuring price movement over time.
5. Bollinger Bands – Uses standard deviations to create bands around a moving average, indicating volatility levels.
These indicators help traders assess risk and potential price movements in options trading.
How can traders profit from volatility in options?
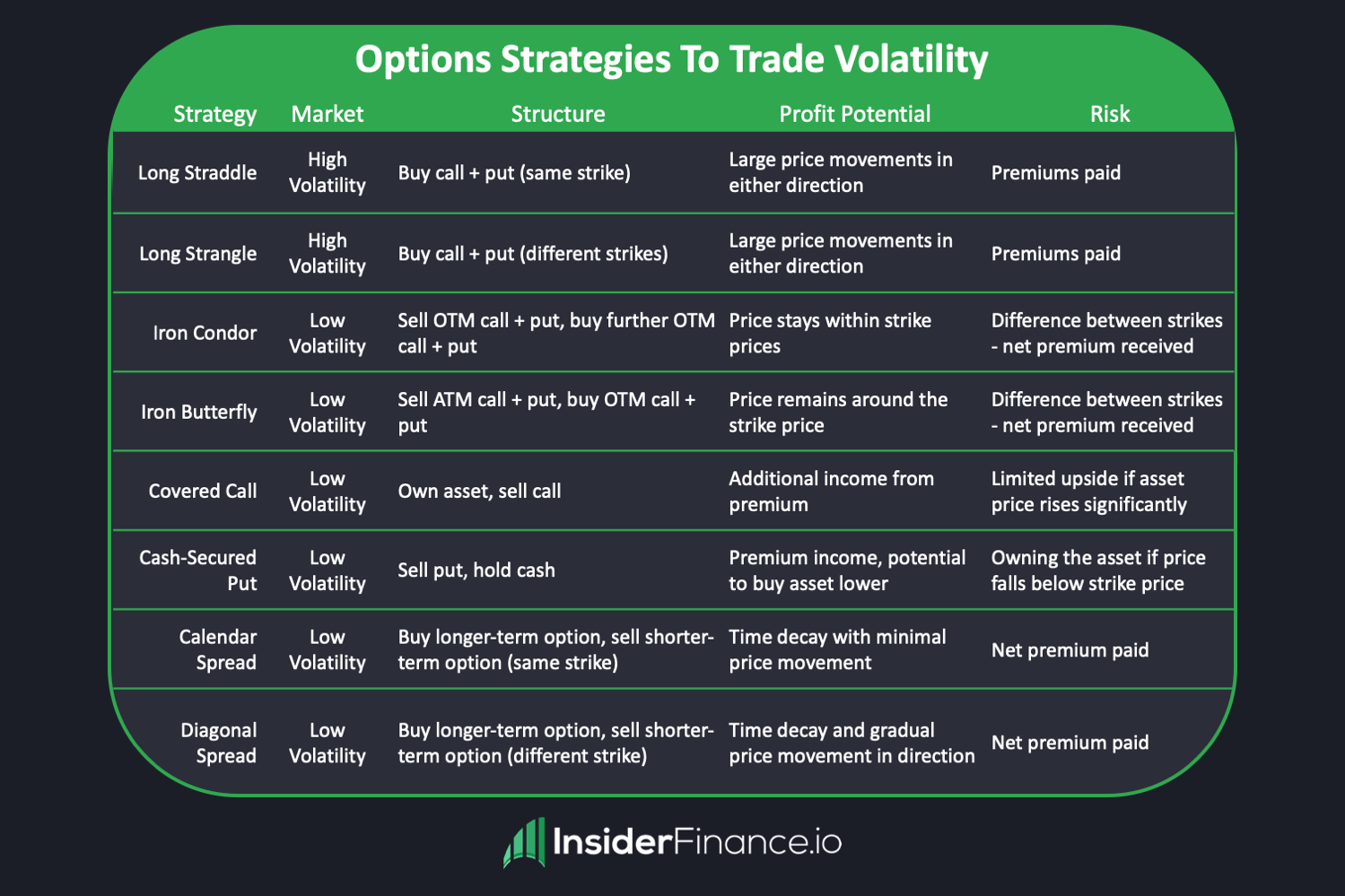
Traders can profit from volatility in options by employing strategies like straddles and strangles. These strategies involve buying both call and put options on the same asset, capitalizing on significant price movements. When volatility increases, option premiums rise, allowing traders to sell these options at a profit. Additionally, traders can use volatility indicators, like the VIX, to identify potential spikes and adjust their positions accordingly. Timing is crucial; entering trades before anticipated volatility events, such as earnings reports or economic announcements, can yield significant returns.
What are the risks of trading options in volatile markets?
Trading options in volatile markets carries several risks. First, rapid price swings can lead to significant losses if positions move against you. Second, implied volatility can inflate option premiums, making it costly to enter trades. Third, sudden market shifts may trigger stop-loss orders, resulting in slippage. Fourth, liquidity can decrease, making it harder to execute trades at desired prices. Finally, the psychological strain of volatility can lead to impulsive decisions, amplifying risk.
How can I manage risk with volatile options?
To manage risk with volatile options in day trading, focus on these strategies:
1. Position Sizing: Limit your investment per trade to a small percentage of your total capital to minimize potential losses.
2. Use Stop-Loss Orders: Set stop-loss orders to automatically exit trades at predefined loss levels, protecting your capital.
3. Diversification: Spread your investments across different options to reduce exposure to any single asset's volatility.
4. Trade Liquid Options: Stick to options with high liquidity to ensure you can enter and exit positions easily without large spreads.
5. Monitor Implied Volatility: Pay attention to implied volatility changes, as high volatility can inflate option premiums, affecting your entry and exit points.
6. Consider Spreads: Use option spreads (like bull call or bear put spreads) to limit potential losses while still gaining from volatility.
7. Stay Informed: Keep up with market news and events that could impact volatility, adjusting your strategies accordingly.
Implementing these tactics will help you navigate the risks associated with volatile options more effectively.
## How Does Volatility Affect Options Trading in Day Trading?
Volatility impacts day trading options by increasing premium prices and potential profit opportunities. Higher volatility leads to wider price swings, which can enhance the chance of profitable trades. However, it also increases risk, as price movements can be unpredictable. Traders often use volatility indicators to inform their strategies.
Learn more about: Understanding Options in Day Trading
Learn about How Does Insider Trading Affect Day Traders?
What is the difference between implied and historical volatility?
Implied volatility reflects the market's expectations of future volatility based on option prices, while historical volatility measures past price movements of the underlying asset. In day trading options, high implied volatility can lead to higher option premiums, indicating greater risk and potential reward. Conversely, historical volatility helps traders understand how much the asset has fluctuated in the past, providing context for current market conditions. Both types of volatility are crucial for making informed trading decisions.
How does earnings season affect volatility in options trading?

Earnings season increases volatility in options trading due to heightened uncertainty around a company's performance. Traders anticipate significant price swings based on earnings reports, leading to increased demand for options. This demand often inflates implied volatility, making options pricier. Consequently, traders may experience larger gains or losses as stock prices react to the earnings announcements, driving both risk and opportunity in day trading.
What are the effects of market news on option volatility?
Market news significantly affects option volatility by causing rapid price fluctuations. Positive news typically leads to increased volatility as traders react, while negative news can create uncertainty, further amplifying volatility. Events like earnings reports or economic indicators often result in sharp spikes or drops in option premiums. This volatility can present opportunities for day traders, allowing them to capitalize on short-term price movements. However, it also increases risk, as unexpected news can lead to substantial losses. Understanding the relationship between market news and option volatility is crucial for effective day trading strategies.
How do I use volatility skew in options trading?
To use volatility skew in options trading, start by analyzing the implied volatility (IV) across different strike prices and expiration dates. Look for patterns—higher IV for out-of-the-money (OTM) puts indicates bearish sentiment, while higher IV for OTM calls suggests bullish sentiment.
Incorporate this insight into your strategy: if you see a steep skew favoring puts, consider selling OTM puts to capitalize on potential IV contraction. Conversely, if calls are skewed high, think about buying OTM calls to benefit from rising volatility.
Adjust your trades based on market conditions and the skew's behavior. Always monitor changes in IV after key events or announcements, as they can significantly impact your options' pricing and risk.
What tools can help analyze volatility for day trading options?
Tools that can help analyze volatility for day trading options include:
1. Bollinger Bands: These show price volatility and help identify overbought or oversold conditions.
2. Implied Volatility (IV) Charts: These display market expectations of future volatility, crucial for options pricing.
3. Average True Range (ATR): This measures market volatility by calculating price range movements over time.
4. Options Analytics Software: Platforms like Thinkorswim or TradeStation offer volatility analysis tools and options pricing models.
5. Volatility Index (VIX): Often referred to as the "fear gauge," it measures market volatility and can guide options strategies.
6. Technical Indicators: Tools like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) can help gauge market momentum and volatility trends.
Using these tools can enhance your understanding of market fluctuations and improve day trading strategies.
Conclusion about Impact of Volatility on Day Trading Options
In summary, volatility is a crucial factor in day trading options, significantly influencing option pricing and trading strategies. Understanding both implied and historical volatility allows traders to make informed decisions, particularly during periods of heightened market activity. By employing effective strategies and risk management techniques, traders can capitalize on market fluctuations while minimizing potential losses. For comprehensive insights and guidance on navigating these complexities, consider the resources available at DayTradingBusiness.
Learn about The Impact of Volatility on Day Trading Risks