Did you know that trading without paying attention to volume is like trying to swim with one arm tied behind your back? In day trading ETFs, understanding volume is crucial for making informed decisions. This article dives into the fundamentals of volume in ETF trading, explaining its significance, how to analyze trends, and the best tools for tracking it. You'll learn how volume impacts trading signals, price movements, and volatility, as well as how to identify key patterns and avoid common misconceptions. Maximize your trading strategies with insights from DayTradingBusiness on effectively using volume to enhance your ETF trading success.
What is volume in day trading ETFs?
Volume in day trading ETFs refers to the number of shares traded within a specific time frame, usually a day. High volume indicates strong interest and liquidity, making it easier to enter and exit positions. Day traders use volume to confirm trends; for instance, rising prices with increasing volume suggest a strong upward trend. Conversely, if prices rise but volume decreases, it may signal a potential reversal. Monitoring volume helps traders make informed decisions and manage risk effectively.
How does volume impact ETF trading decisions?
Volume impacts ETF trading decisions by indicating market interest and liquidity. High volume often signals strong investor interest, making it easier to enter and exit positions without significant price changes. Traders use volume to confirm trends; for instance, rising prices accompanied by increasing volume suggest a strong uptrend. Conversely, if prices rise but volume declines, it may indicate a weakening trend. Volume can also highlight potential reversals; sudden spikes can signal impending price changes. Incorporating volume analysis helps traders make informed entry and exit decisions in day trading ETFs.
Why is volume important for day trading ETFs?
Volume is crucial for day trading ETFs because it indicates the strength of price movements. High volume often confirms trends, signaling that a price change is likely to continue, while low volume can suggest weakness and potential reversals. It helps traders identify entry and exit points, ensuring they trade when there's enough liquidity to execute orders efficiently. Additionally, volume can reveal investor sentiment, allowing traders to make informed decisions based on market activity.
How can I analyze volume trends in ETFs?
To analyze volume trends in ETFs, start by examining daily trading volume data alongside price movement. Look for volume spikes, which often indicate strong interest or potential price reversals. Use moving averages of volume to identify trends; for example, compare the current volume to the 20-day average. Also, consider volume in conjunction with price: increasing volume with rising prices suggests strength, while increasing volume with falling prices may indicate weakness. Tools like volume oscillators or the On-Balance Volume (OBV) can provide deeper insights into buying and selling pressure. Finally, track volume patterns during key market events or earnings reports for additional context.
What are the best tools for tracking ETF volume?
The best tools for tracking ETF volume include:
1. Brokerage Platforms: Most brokers like TD Ameritrade, E*TRADE, and Charles Schwab provide detailed volume data for ETFs.
2. Market Data Websites: Sites like Yahoo Finance and MarketWatch offer real-time volume information and charts.
3. Trading Software: Tools like TradingView and Thinkorswim offer advanced charting capabilities with volume overlays.
4. Stock Screeners: Use screeners like Finviz or StockCharts to filter ETFs by volume metrics.
5. Mobile Apps: Apps like Robinhood and Webull provide easy access to volume data on the go.
Utilizing these tools can help you effectively analyze ETF volume for day trading strategies.
How do I interpret high volume in ETF trading?
High volume in ETF trading indicates strong investor interest and can signal potential price movement. It often reflects increased buying or selling pressure, suggesting that a trend might continue or reverse. For day trading, high volume can confirm the strength of a breakout or breakdown. Monitor volume spikes alongside price changes; if the price moves up with high volume, it’s a bullish sign, while high volume on a price drop may indicate bearish sentiment. Always consider volume in conjunction with other indicators for more accurate trading decisions.
What does low volume indicate in ETF markets?
Low volume in ETF markets indicates reduced investor interest and liquidity. This can lead to wider bid-ask spreads, making it harder to enter or exit positions without impacting the price. Low volume may also signal potential price manipulation or increased volatility, as small trades can cause larger price swings. For day trading, it's crucial to focus on ETFs with higher volume to ensure smoother transactions and more reliable price movements.
How can I use volume to confirm trading signals?
To use volume to confirm trading signals in day trading ETFs, follow these steps:
1. Look for Volume Spikes: When a price breakout occurs, check for a corresponding increase in volume. A spike indicates strong interest and confirms the signal.
2. Analyze Volume Trend: Compare current volume to its average over a set period. High volume with price increases suggests bullish momentum, while high volume with price decreases indicates bearish sentiment.
3. Volume Divergence: Watch for divergence between price and volume. If prices rise but volume falls, it may signal a potential reversal.
4. Use Volume Indicators: Incorporate tools like On-Balance Volume (OBV) or Volume Moving Average to gauge the strength of price movements.
5. Confirm with Multiple Time Frames: Check volume trends across different time frames. Consistent volume patterns across short and long-term charts strengthen your signal.
By integrating these volume strategies, you can enhance the reliability of your trading signals in ETFs.
What volume patterns should I look for in ETFs?
Look for volume spikes during price breaks, indicating strong interest. High volume on uptrends suggests bullish momentum, while high volume on downtrends can signal bearish sentiment. Pay attention to average volume; sudden increases above this can indicate potential reversals or continuations. Confirm breakouts with volume; if a breakout occurs with low volume, it may lack strength. Also, watch for volume convergence or divergence with price trends to spot potential reversals.
How does volume affect ETF price movement?
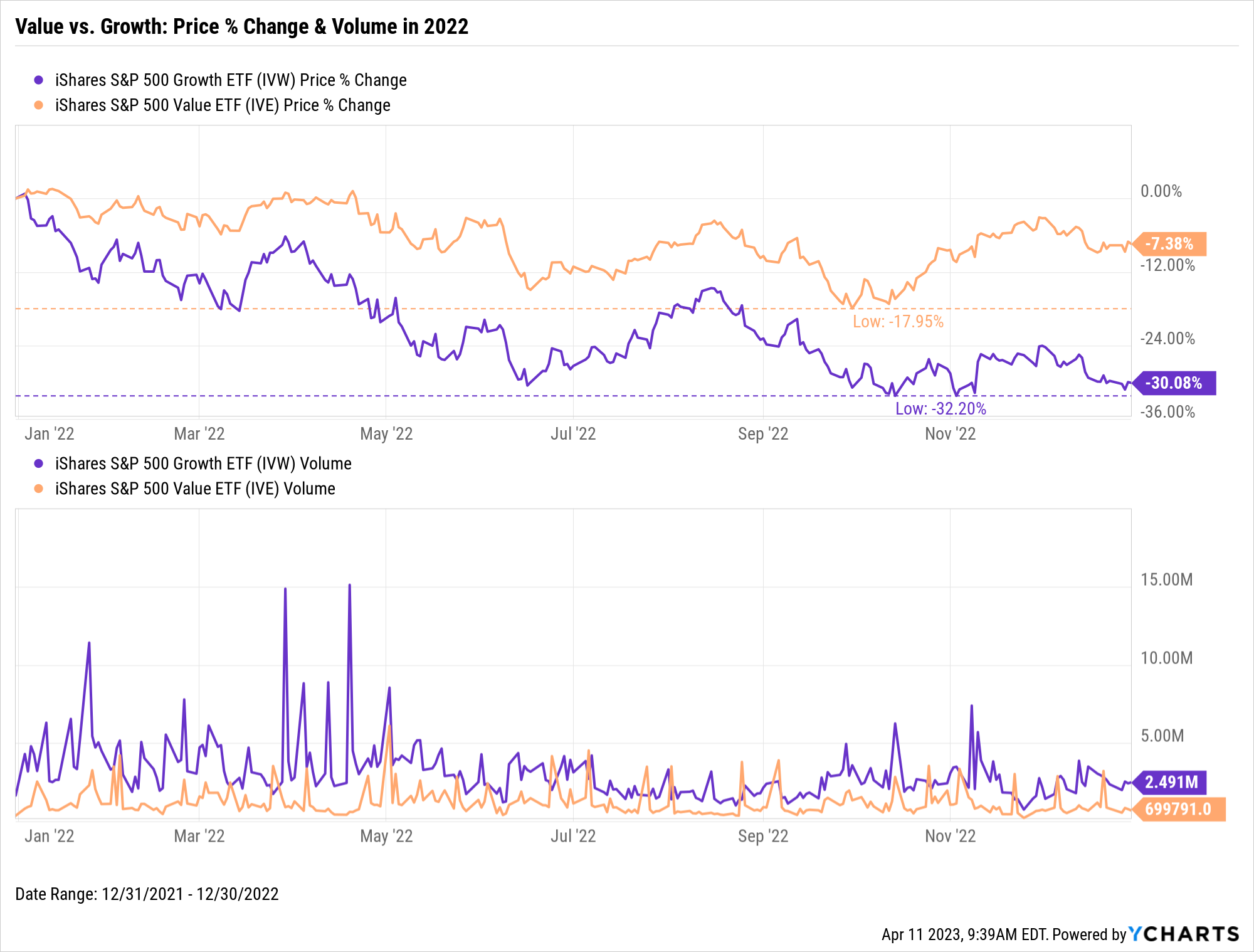
Volume affects ETF price movement by indicating the strength of a price trend. High volume often signals strong interest and can lead to more significant price changes, while low volume may result in less price stability and more erratic movements. In day trading ETFs, traders look for increased volume to confirm trends or reversals, as it often precedes substantial price action. For instance, if an ETF sees a spike in volume during an upward trend, it suggests buyer confidence, potentially driving prices higher. Conversely, low volume during a dip may indicate weak selling pressure, allowing for potential recovery. Monitoring volume helps traders make informed decisions about entry and exit points.
Can I day trade ETFs with low volume?
Yes, you can day trade ETFs with low volume, but it comes with risks. Low volume often means less liquidity, which can lead to wider bid-ask spreads and more slippage. This can make it harder to enter and exit positions at desired prices. To manage risks, consider using limit orders and be aware of the potential for price manipulation. Always analyze volume trends and market conditions before trading.
What Are the Best ETFs for Day Trading Using Volume Indicators?
The best ETFs for day trading typically include high-volume, liquid options such as SPY (S&P 500 ETF), QQQ (NASDAQ-100 ETF), and IWM (Russell 2000 ETF). To use volume in day trading ETFs, focus on spikes in volume to identify potential price movements, confirm trends, and validate entry and exit points. Look for ETFs with an average daily volume of at least 1 million shares for optimal liquidity.
Learn more about: What Are the Best ETFs for Day Trading?
Learn about Best Practices for Conducting Volume Analysis in Day Trading
How do volume spikes influence ETF trading?
Volume spikes in ETF trading indicate heightened interest and activity, often leading to increased volatility. When volume surges, it can signal potential price movements or reversals. Traders often use these spikes to confirm entry or exit points, as they suggest strong market sentiment. For day trading ETFs, high volume can enhance liquidity, allowing for quicker trades and tighter spreads. Monitoring volume alongside price action helps identify trends and potential breakouts, making it a crucial element in trading strategies.
What role does volume play in volatility for ETFs?
Volume indicates the number of shares traded in an ETF and is crucial for assessing volatility. Higher volume often correlates with increased volatility, as it reflects greater investor interest and activity. In day trading, watching volume helps identify potential price movements; low volume can lead to erratic price changes, while high volume typically signals stronger trends. Use volume to confirm breakout patterns or reversals; if an ETF surges on high volume, it likely indicates a sustained move, while low-volume moves may be less reliable.
How can I combine volume analysis with technical indicators?
Combine volume analysis with technical indicators by following these steps:
1. Identify Volume Trends: Look for increasing volume on price movements to confirm trends. If the price rises with high volume, it signals strength.
2. Use Moving Averages: Apply moving averages (like the 50-day or 200-day) to smooth price data. When the price crosses above a moving average with high volume, it can indicate a bullish signal.
3. Integrate RSI: Use the Relative Strength Index (RSI) alongside volume. If RSI shows overbought or oversold conditions while volume spikes, it can help confirm potential reversals.
4. Monitor Volume Oscillators: Use tools like the Chaikin Money Flow or On-Balance Volume to gauge buying and selling pressure relative to price movements.
5. Check for Divergence: Look for divergence between price and volume indicators. If prices rise but volume decreases, this may suggest a weakening trend.
6. Set Entry and Exit Points: Use volume in conjunction with indicators to set clear entry and exit points. For example, enter a trade when price breaks resistance on high volume.
By effectively combining volume analysis with these technical indicators, you can enhance your decision-making in day trading ETFs.
Learn about How to Combine Fundamental and Technical Analysis in Day Trading
What are common misconceptions about volume in ETF trading?
Common misconceptions about volume in ETF trading include:
1. High Volume Always Means Strong Interest: Traders often assume that high volume indicates strong buying or selling interest, but it can also signal panic or forced selling.
2. Volume Alone Determines Price Direction: Many believe that volume alone dictates price trends. In reality, volume must be analyzed alongside price action and market context.
3. Low Volume Equals Poor Investment: Some think low volume ETFs are always a bad investment. However, low volume can indicate stability or niche interest without necessarily being a red flag.
4. Volume Patterns Are Universal: Traders may think volume patterns apply the same across all ETFs. Each ETF can behave differently based on its underlying assets and market conditions.
5. Post-News Volume Is Always Significant: Some assume spikes in volume after news are always positive indicators. This can lead to buying into volatility without considering potential reversals.
Understanding these misconceptions can help traders make more informed decisions when using volume in day trading ETFs.
How can I improve my day trading strategy using volume?
To improve your day trading strategy using volume in ETFs, focus on these key points:
1. Volume Confirmation: Use volume to confirm price movements. A price increase accompanied by high volume suggests strong buying interest, while low volume may indicate weakness.
2. Volume Spikes: Identify volume spikes that often precede significant price changes. Look for unusual trading activity before key news or earnings reports.
3. Volume Indicators: Utilize volume-based indicators like the On-Balance Volume (OBV) or Volume Moving Averages to spot trends and potential reversals.
4. Support and Resistance: Analyze volume at support and resistance levels. High volume at these points can indicate strong buying or selling pressure, helping you make better entry and exit decisions.
5. Market Sentiment: Monitor overall market volume to gauge sentiment. Increased volume in the broader market can validate your ETF trades.
6. Trade Size: Adjust your position size based on volume trends. In high-volume conditions, you might increase your trade size, while in low-volume situations, consider smaller positions.
7. Volume and Timeframes: Tailor your strategy to different timeframes. Shorter timeframes can reveal immediate volume trends, while longer ones help identify overall patterns.
By integrating these volume strategies into your day trading, you can enhance your decision-making and improve your overall performance.
Learn about How Market Microstructure Insights Improve Day Trading Accuracy
Conclusion about How to Use Volume in Day Trading ETFs
Understanding volume is crucial for successful day trading of ETFs. It not only informs trading decisions but also helps in confirming signals and recognizing patterns that can lead to profitable trades. By leveraging the right tools and analyzing volume trends, traders can enhance their strategies and navigate the market more effectively. For those seeking deeper insights and guidance, DayTradingBusiness offers valuable resources to refine your trading approach and improve your overall performance in the ETF market.
Learn about How to Use Volume to Improve Day Trading