Did you know that the average person spends about a year of their life waiting for red lights to turn green? Just like waiting for that green light, choosing between active and passive ETFs for day trading can be a pivotal decision. This article dives into the essential differences between active and passive ETFs, exploring their unique benefits, fee structures, and liquidity factors. We’ll also cover performance metrics, tax implications, and the influence of market conditions and volatility on each type. By the end, you'll have a clearer understanding of which ETF suits your day trading strategy best, empowering you to make informed decisions with insights from DayTradingBusiness.
What are Active ETFs and Passive ETFs?
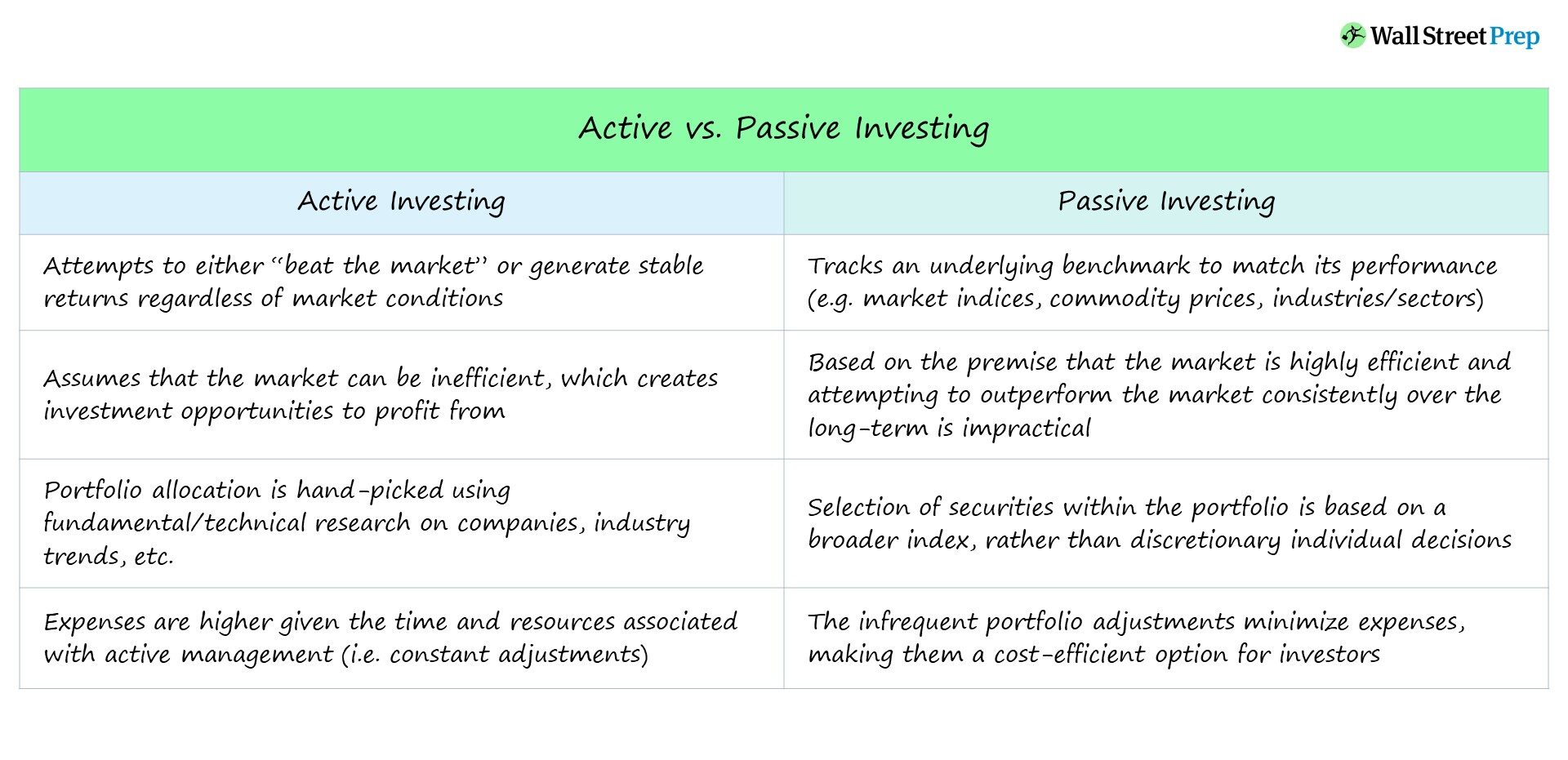
Active ETFs are funds managed by professionals who make investment decisions based on research and market analysis. They aim to outperform a benchmark index through strategic buying and selling. Passive ETFs, on the other hand, track a specific index and aim to replicate its performance with minimal management.
For day trading, active ETFs can offer more opportunities for quick gains due to their responsive management, while passive ETFs provide lower fees and consistent performance, making them less volatile but potentially less profitable in the short term. Choose active ETFs for agility and potential higher returns; opt for passive ETFs for lower costs and stability.
How do Active ETFs differ from Passive ETFs?
Active ETFs are managed by a team making investment decisions based on market analysis, aiming to outperform a benchmark. Passive ETFs, on the other hand, track a specific index and aim to replicate its performance. For day trading, Active ETFs can offer more opportunities for higher returns due to their dynamic management, while Passive ETFs provide stability and lower fees. Active ETFs may experience more volatility, while Passive ETFs generally have lower expense ratios and predictable performance.
What are the benefits of Active ETFs for day trading?
Active ETFs offer several benefits for day trading. They provide the potential for higher returns through active management, allowing traders to capitalize on market fluctuations. Their intraday liquidity enables quick entry and exit, which is crucial for day trading strategies. Additionally, active ETFs often have lower tracking errors compared to passive ETFs, allowing for more precise alignment with market trends. They can also be more responsive to market news and events, giving day traders an edge. Overall, active ETFs combine flexibility and responsiveness, making them suitable for fast-paced trading environments.
What are the advantages of Passive ETFs for day trading?
Passive ETFs offer lower fees, which can enhance profitability in day trading. They typically have tighter bid-ask spreads, facilitating quicker trades. Their predictable performance reduces risk, allowing traders to focus on technical analysis rather than management strategies. Additionally, passive ETFs often have higher liquidity, making it easier to enter and exit positions swiftly. This combination of cost efficiency, speed, and reliability makes passive ETFs an attractive choice for day traders.
Which type of ETF is more suitable for day trading?
Active ETFs are more suitable for day trading. They typically have higher volatility, which can provide better short-term price movements and opportunities. Additionally, active management aims to capitalize on market inefficiencies, making them more responsive to daily market changes compared to passive ETFs, which track indices and may not react as quickly.
How do fees compare between Active and Passive ETFs?
Active ETFs typically have higher fees than passive ETFs. This is due to the active management strategy, which involves frequent trading and research costs. Passive ETFs, on the other hand, usually track an index and have lower expense ratios. For day trading, lower fees in passive ETFs can enhance profitability, while the potential for higher returns in active ETFs comes with increased costs.
What role does liquidity play in Active vs. Passive ETFs?
Liquidity is crucial in both Active and Passive ETFs, especially for day trading.
In Passive ETFs, liquidity ensures tighter bid-ask spreads and easier entry and exit points, which is vital for traders looking to capitalize on short-term price movements. Higher trading volumes typically lead to better liquidity in these funds.
Active ETFs, while often less liquid than their passive counterparts, rely on liquidity to execute trades efficiently. Active managers might trade more frequently, so liquidity impacts their ability to adjust positions without affecting the market price significantly.
For day trading, choosing liquid ETFs—whether active or passive—helps minimize slippage and enhances the potential for profit.
How do performance metrics differ for Active and Passive ETFs?
Active ETFs typically have higher performance metrics due to active management strategies that aim to outperform benchmarks. They may exhibit greater volatility and potential for higher returns, but also come with higher fees. Passive ETFs, on the other hand, aim to match market performance, resulting in lower costs and more consistent returns that closely track an index. For day trading, active ETFs might offer more opportunities for quick gains, while passive ETFs provide stability and lower risk.
What are the tax implications of Active and Passive ETFs?
Active ETFs typically generate more capital gains due to frequent trading, leading to higher tax liabilities for investors. These gains are taxed at short-term rates if held for less than a year. Passive ETFs, on the other hand, usually have lower turnover, resulting in fewer capital gains distributions, which can be taxed at long-term rates if held for over a year. For day trading, the active approach may lead to higher tax burdens, while passive strategies can be more tax-efficient.
How can volatility impact Active and Passive ETFs?
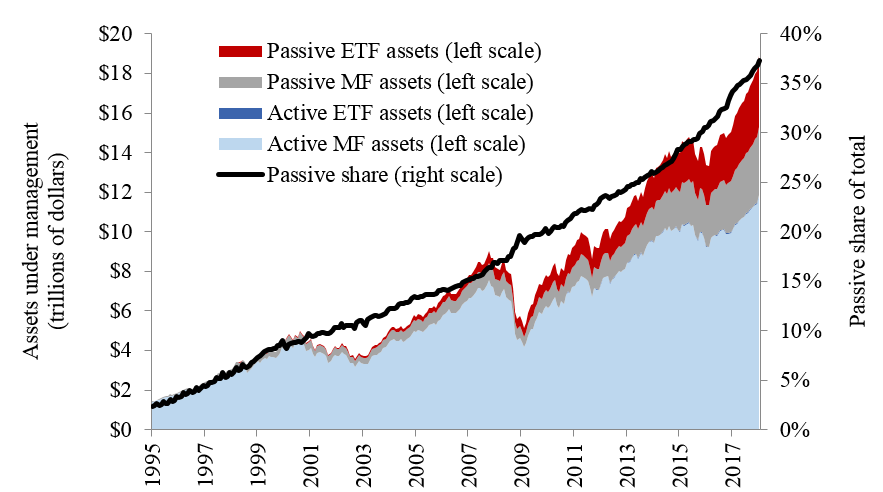
Volatility affects Active and Passive ETFs differently in day trading. Active ETFs can capitalize on rapid price movements, allowing managers to make quick trades for potential profit. This adaptability can lead to higher returns during volatile periods. Conversely, Passive ETFs track an index and may not react swiftly to market changes, potentially missing out on gains. However, they tend to be less risky and more stable during turbulent times, appealing to conservative traders. Overall, volatility can enhance Active ETF performance while posing risks for Passive ETFs.
Are there specific strategies for trading Active ETFs?
Yes, specific strategies for trading Active ETFs include:
1. Monitor Market Trends: Keep an eye on sector performance and economic indicators to identify which Active ETFs may outperform.
2. Liquidity Analysis: Choose Active ETFs with high trading volumes to ensure you can enter and exit positions easily.
3. Use Technical Analysis: Apply chart patterns, moving averages, and volume analysis to find entry and exit points.
4. Understand Fund Manager Strategy: Research the manager’s investment style and strategy, as this can impact performance.
5. Watch for News Events: Be aware of earnings reports, economic data releases, and geopolitical events that can influence the ETFs.
6. Set Stop-Loss Orders: Protect your capital from significant losses by setting stop-loss orders based on your risk tolerance.
7. Diversify Across Sectors: Spread your investments across different sectors to mitigate risk and capture broader market movements.
8. Review Holdings Regularly: Active ETFs can change their holdings; stay updated on these changes to align with your trading strategy.
What are the best active and passive ETFs for day trading?
The best ETFs for day trading typically include those with high liquidity and volatility. Popular options are the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY), Invesco QQQ Trust (QQQ), and iShares Russell 2000 ETF (IWM). Active ETFs, which can adjust holdings frequently, may offer better short-term opportunities, while passive ETFs typically track an index and may provide stability. Compare both based on your trading strategy and risk tolerance.
Learn more about: What Are the Best ETFs for Day Trading?
Learn about What Are the Best ETFs for Day Trading?
What strategies work best for trading Passive ETFs?
For trading Passive ETFs, focus on these strategies:
1. Technical Analysis: Use charts and indicators to identify trends and entry/exit points. Look for patterns like moving averages or support/resistance levels.
2. Market Timing: Monitor market conditions and news that may affect the ETF. Be ready to act quickly to capitalize on short-term price movements.
3. Liquidity: Choose highly liquid ETFs to ensure tight spreads and easier execution of trades. Avoid thinly traded funds to reduce slippage.
4. Diversification: Trade a mix of sectors or asset classes within passive ETFs to mitigate risk while capturing market movements.
5. Limit Orders: Use limit orders to control entry and exit prices, reducing the risk of sudden market fluctuations.
6. Momentum Trading: Identify ETFs that are showing strong momentum and ride the trend until signs of reversal appear.
7. Risk Management: Set stop-loss orders to protect your capital and define your risk-reward ratio before entering trades.
These strategies can enhance your effectiveness when trading Passive ETFs, allowing you to navigate the market efficiently.
How do market conditions affect Active and Passive ETF performance?
Market conditions significantly impact Active and Passive ETF performance.
In volatile markets, Active ETFs can outperform because managers adjust strategies quickly to capitalize on price swings. They can take advantage of short-term trends or hedge against downturns.
Conversely, Passive ETFs typically lag in volatile conditions since they follow a set index without making tactical changes. They may experience sharper declines during market downturns but can recover as the market stabilizes.
In stable markets, Passive ETFs often perform better due to lower fees and consistent tracking of indices. Active ETFs may struggle with high management costs and the challenge of consistently beating the market.
For day trading, understanding these dynamics is crucial. Active ETFs can offer opportunities for profit in fluctuating markets, while Passive ETFs serve best when markets are stable.
Learn about How Market Conditions Affect HFT Strategies
What are common risks associated with Active ETFs?
Common risks associated with Active ETFs include higher management fees, which can reduce returns, and increased volatility due to active trading strategies. There's also the risk of underperformance compared to benchmarks, as active managers may not consistently outperform passive alternatives. Additionally, liquidity risks can arise if the ETF holds less liquid securities, making it harder to buy or sell shares without affecting the price. Lastly, market risk remains a factor, as active ETFs are still subject to overall market fluctuations.
What risks should traders consider with Passive ETFs?
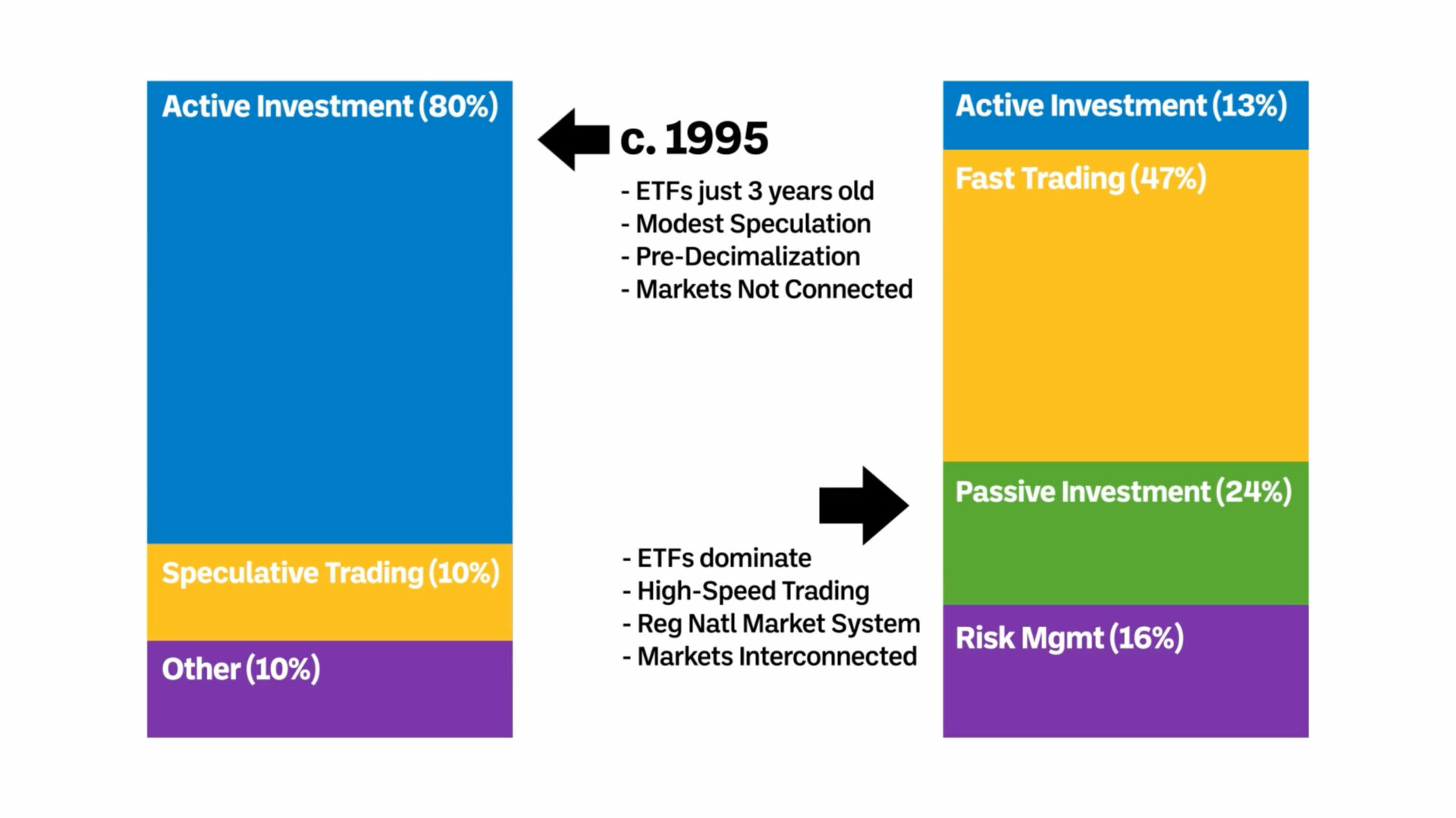
Traders should consider several risks with passive ETFs. First, passive ETFs track an index, which means they can underperform in volatile markets or during downturns. Second, they lack flexibility; if the index includes underperforming stocks, the ETF will too. Third, liquidity can be an issue—some passive ETFs may have lower trading volumes, leading to wider bid-ask spreads. Finally, market risk remains; if the overall market declines, passive ETFs will follow suit.
How can investors decide between Active and Passive ETFs for day trading?
Investors should consider several factors when deciding between Active and Passive ETFs for day trading.
Active ETFs aim to outperform a benchmark through strategic trading and can react quickly to market changes, offering potential for higher returns, but they come with higher fees and risk.
Passive ETFs mirror an index, providing lower costs and predictable performance, which can be beneficial for consistent trading strategies.
Evaluate your trading style: if you seek quick gains and are comfortable with higher volatility, Active ETFs may suit you. If you prefer stability and lower expenses, go for Passive ETFs.
Also, consider liquidity, trading volume, and expense ratios as they impact your trading efficiency. Ultimately, align your choice with your risk tolerance, trading goals, and market knowledge.
Conclusion about Comparing Active vs. Passive ETFs for Day Trading
In summary, choosing between Active and Passive ETFs for day trading hinges on individual trading strategies and goals. Active ETFs offer the potential for higher returns through active management, while Passive ETFs provide stability and lower fees. Understanding their liquidity, performance metrics, and risks is essential for making informed decisions. Ultimately, aligning your choice with your trading style will enhance your success. For expert insights and tailored strategies, consider the resources provided by DayTradingBusiness to navigate your trading journey effectively.
Learn about Day Trading vs. Long-Term Investing in ETFs