Did you know that even the stock market has its own version of a traffic jam? Just like cars stuck in rush hour, order flow can get congested, affecting how prices move. In this article, we dive deep into the concept of order flow and its microstructure implications, exploring what order flow is and how it influences price movements. We’ll discuss the importance of order flow for traders, key components, and how bid and ask sizes impact market liquidity. Additionally, we’ll examine the role of market makers, the effects on bid-ask spreads, and common order types in microstructure analysis. Learn how order flow data can predict short-term price changes, the significance of order flow imbalance, and the strategies utilized by high-frequency traders. Finally, we’ll cover the risks of relying on order flow signals, tools for analysis, behavior across asset classes, and how mastering order flow can enhance your trading strategies—all brought to you by DayTradingBusiness.
What is order flow in financial markets?
Order flow in financial markets is the stream of buy and sell orders that traders submit to a market. It reveals the real-time supply and demand, showing how traders are positioning themselves. Analyzing order flow helps identify market sentiment, potential price moves, and liquidity levels. It’s the behind-the-scenes activity that drives price changes, reflecting traders’ intentions before trades are executed.
How does order flow influence price movements?
Order flow directly impacts price movements by revealing buy and sell pressures in real-time. When buyers outnumber sellers, prices tend to rise; more sellers push prices down. Large orders or sudden shifts in order flow can cause rapid price changes or reversals. It reflects market sentiment and liquidity, guiding traders on potential trend strength or reversals. Essentially, order flow acts as the market’s heartbeat, dictating short-term price direction through the imbalance of incoming orders.
Why is order flow important for traders?
Order flow reveals real-time buying and selling activity, helping traders see market momentum. It shows where large trades happen, indicating potential price moves before they occur. Understanding order flow helps traders spot support and resistance levels based on actual market liquidity. It provides insight into trader behavior and market sentiment, allowing for more precise entry and exit points. Essentially, order flow offers a microscopic view of market microstructure, giving traders an edge over relying solely on price charts.
What are the key components of order flow microstructure?
The key components of order flow microstructure are bid-ask spreads, order book depth, order types (market, limit, stop), order arrival rates, and trade execution algorithms.
How do bid and ask sizes affect market liquidity?
Bid and ask sizes directly impact market liquidity by indicating how much volume is available at each price level. Larger bid and ask sizes mean more buy and sell interest, making it easier to execute large trades without moving prices. Small sizes can cause price jumps and reduce liquidity, as there’s less volume to absorb trades. When bid or ask sizes fluctuate, they signal shifts in supply and demand, affecting the ease of entering or exiting positions. High bid and ask sizes typically lead to tighter spreads and smoother price movements, enhancing overall market liquidity.
What role do market makers play in order flow?
Market makers facilitate order flow by providing liquidity, matching buy and sell orders to keep markets smooth. They step in when there's imbalance, absorbing excess buy or sell pressure to prevent wild price swings. Their presence ensures that traders can execute large orders without causing major price disruptions, stabilizing the order book. This active management of order flow helps maintain market efficiency and tight spreads.
How does order flow impact bid-ask spreads?
Order flow influences bid-ask spreads by revealing supply and demand dynamics. When buy and sell orders are balanced, spreads tighten because liquidity is high. Heavy buying or selling pressure causes spreads to widen as market makers protect against volatility. Sudden shifts in order flow can lead to wider spreads, reflecting increased risk and lower liquidity. Consistent order flow signals confidence, narrowing the gap between bid and ask prices.
What are the common order types in microstructure analysis?
Common order types in microstructure analysis are market orders, limit orders, and stop orders. Market orders execute immediately at the best available price. Limit orders set a specific price for buying or selling, adding liquidity. Stop orders trigger a market order once a certain price is reached, often used for risk management.
How can order flow data predict short-term price changes?
Order flow data shows real-time buying and selling activity, revealing market sentiment before price moves happen. Large buy orders indicate upward pressure, while heavy sell orders signal potential drops. Tracking order flow helps traders spot shifts in supply and demand, predicting short-term price changes. For example, a surge in buy orders can precede a quick rally, while increasing sell orders may trigger a short-term dip. It provides a detailed view of market microstructure, allowing for more accurate, immediate predictions of price movement.
What is the significance of order flow imbalance?
Order flow imbalance indicates whether buy or sell orders dominate in a market, signaling potential price movements. It helps traders spot liquidity shifts, anticipate reversals, or confirm trends. A strong imbalance often precedes sharp price changes, making it a crucial tool for understanding market microstructure.
How do high-frequency traders use order flow information?
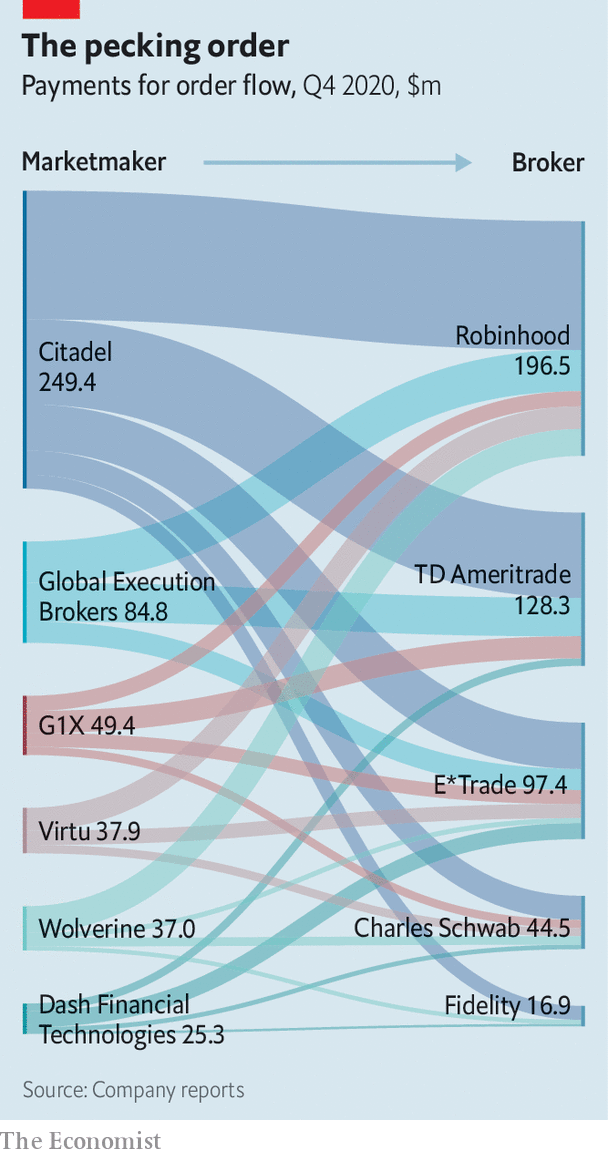
High-frequency traders analyze order flow to detect short-term supply and demand shifts. They monitor real-time buy and sell orders to predict price movements before they happen. By spotting large or unusual order activity, they gain an edge, executing quick trades to capitalize on fleeting opportunities. They use order flow data to identify market imbalances, anticipate breakout points, and refine their entry and exit timing.
Learn about How Do Institutional Traders Use Volume and Order Flow Data?
What are the risks of relying on order flow signals?
Relying on order flow signals risks false signals from market manipulation, leading to wrong trades. It can cause overfitting to short-term noise, missing bigger trends. Liquidity gaps or sudden large orders distort signals, giving a misleading picture. In fast markets, delays or data inaccuracies can lead to poor timing. Overconfidence in order flow may cause ignoring fundamental analysis or broader market context.
How does order flow relate to market depth?
Order flow shows the actual buying and selling activity in the market, reflecting real-time demand and supply. Market depth displays the current order book, showing available bids and asks at different prices. When order flow is strong on the buy side, market depth often shows larger buy orders or rising bid sizes. Conversely, heavy sell order flow can lead to increased ask sizes or price drops. Tracking order flow helps interpret changes in market depth, revealing whether recent trades are pushing the price up or down. They work together: order flow reveals the direction of immediate trades, while market depth shows potential support and resistance levels.
What tools are best for analyzing order flow?
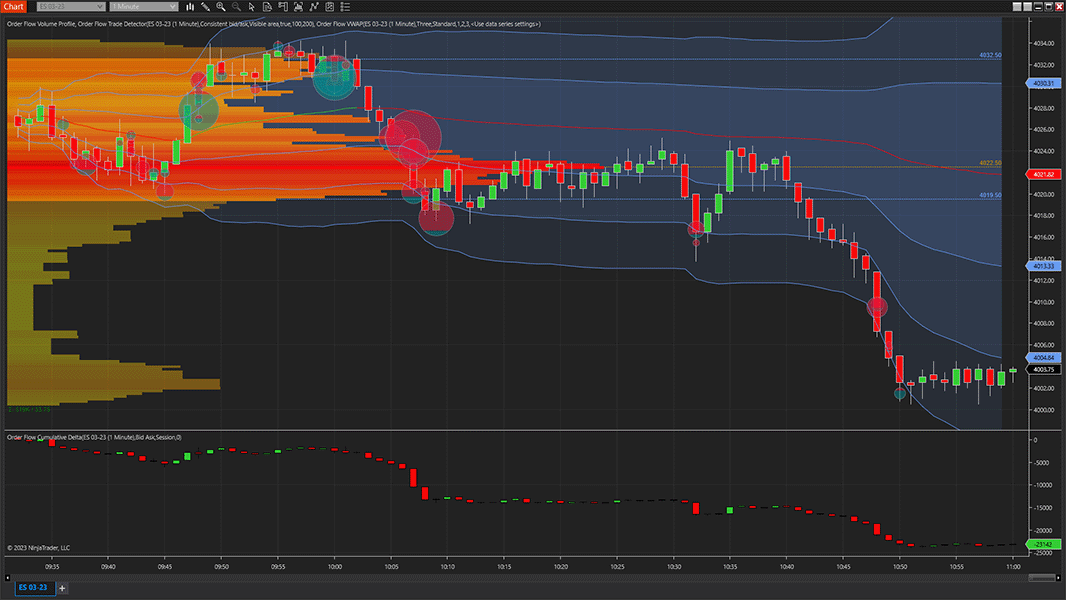
Best tools for analyzing order flow include Bookmap, Sierra Chart, Jigsaw Trading, NinjaTrader, and Quantower. These platforms offer real-time market depth, volume analysis, and order book visualization. They help traders see liquidity changes, identify large orders, and interpret microstructure shifts.
How does order flow behavior differ across asset classes?
Order flow behavior varies by asset class: equities see rapid, high-volume trades with frequent order book updates, while fixed income markets have slower, larger transactions due to lower liquidity. Forex markets operate 24/5 with continuous, high-frequency order flow driven by macroeconomic news, unlike commodities, which often experience sporadic bursts linked to supply and demand shifts. Cryptocurrencies exhibit unpredictable order flow with high volatility and wide spreads, reflecting less mature market microstructure. Each asset class’s order flow reflects its liquidity, trading hours, and market participants, shaping different microstructure dynamics.
Why does understanding order flow improve trading strategies?
Understanding order flow reveals real-time market supply and demand, helping traders anticipate price movements. It exposes hidden liquidity, large trades, and momentum shifts before they hit the chart. By analyzing order flow, traders spot false breakouts, identify key support and resistance, and refine entry and exit points. It provides insight into market sentiment and potential reversals, making strategies more precise and responsive.
Learn about Understanding Order Flow in Day Trading
Conclusion about Understanding Order Flow and Its Microstructure Implications
In conclusion, mastering order flow and its microstructure is essential for traders seeking to enhance their market strategies. By understanding how order flow influences price movements and market liquidity, you can make more informed trading decisions. Analyzing bid and ask sizes, recognizing the role of market makers, and utilizing appropriate tools allow you to predict short-term price changes effectively. For traders looking to gain a competitive edge, insights from order flow analysis can significantly improve overall performance. Leveraging the expertise provided by DayTradingBusiness can further refine your understanding and application of these concepts in your trading practice.