Did you know that the bid-ask spread can sometimes be wider than your favorite pizza's crust? Understanding bid-ask spreads is crucial for day traders, as they directly impact trading costs and strategies. This article dives into what bid-ask spreads are, how they fluctuate based on market conditions, liquidity, and order size, and why they can widen during major news events. Additionally, we explore how to identify narrow spreads and their significance in day trading. With insights from DayTradingBusiness, you'll learn to navigate these spreads effectively, enhancing your trading strategies while minimizing risks.
What is a bid-ask spread in day trading?
The bid-ask spread in day trading is the difference between the highest price buyers are willing to pay (bid) and the lowest price sellers accept (ask). It represents transaction costs and liquidity, affecting how easily you can buy or sell a stock quickly. Narrow spreads mean lower costs and easier trades, while wide spreads increase trading expenses and can slow execution.
How does the bid-ask spread affect trading costs?
The bid-ask spread increases trading costs because you buy at the higher ask price and sell at the lower bid price, losing the difference. A wider spread means higher costs per trade, eating into potential profits. For day traders, narrow spreads reduce expenses, making quick, frequent trades more cost-effective.
Why do bid-ask spreads vary between different stocks?
Bid-ask spreads vary between stocks because of differences in liquidity, trading volume, and market interest. More liquid stocks with high trading volume have narrower spreads since there are many buyers and sellers, making trades easier and cheaper. Less liquid stocks, with lower volume and wider gaps between bid and ask prices, reflect higher risk and lower market activity. Market makers and traders set spreads based on how much risk they take and how quickly they can buy or sell shares without impacting the price. Volatility also widens spreads; if a stock swings wildly, traders want bigger margins to cover potential losses.
How do market conditions influence bid-ask spreads?
Market conditions directly widen or narrow bid-ask spreads. During high volatility or low liquidity, spreads increase because sellers demand higher prices, and buyers want to pay less, reflecting risk and uncertainty. In stable, liquid markets, spreads tighten as both sides agree on prices more easily, reducing transaction costs. Tight spreads often signal healthy trading activity, while wide spreads indicate caution or scarce trading volume.
What role does liquidity play in bid-ask spreads?
Liquidity directly narrows bid-ask spreads by making it easier to buy or sell without causing big price moves. High liquidity means more market participants and larger trading volume, which tightens the spread. Low liquidity widens the spread because fewer buyers and sellers exist, increasing the cost to execute trades smoothly. In day trading, tight spreads from high liquidity help traders enter and exit positions quickly and at minimal cost.
How can I identify a narrow bid-ask spread?
Look for a small difference between the bid and ask prices on the trading platform. A narrow bid-ask spread typically ranges from a few cents to a penny for highly liquid stocks or assets. Check the spread directly on the order book or quote; if the gap is minimal, it's a narrow spread. This indicates high liquidity and low transaction costs, ideal for day trading microstructure.
What is the impact of high volatility on spreads?
High volatility widens bid-ask spreads because market makers risk more, so they charge higher costs to compensate. This increase makes it more expensive to buy or sell quickly, reducing liquidity and trading efficiency.
How do bid-ask spreads differ in various trading hours?
Bid-ask spreads are narrower during peak trading hours when liquidity is highest, making it easier to buy and sell quickly. In early morning or late evening, spreads widen as trading volume drops, increasing transaction costs. During high-volume periods, tight spreads reflect active market participation; during low-volume times, wider spreads indicate less liquidity and higher costs.
Why do bid-ask spreads widen during news releases?
Bid-ask spreads widen during news releases because traders become uncertain about the stock’s direction. This increased uncertainty makes market makers more cautious, so they ask for higher premiums to take on risk. Reduced liquidity and fewer willing counterparties also push spreads wider, as participants hesitate to trade until the market stabilizes.
How does order size affect the bid-ask spread?
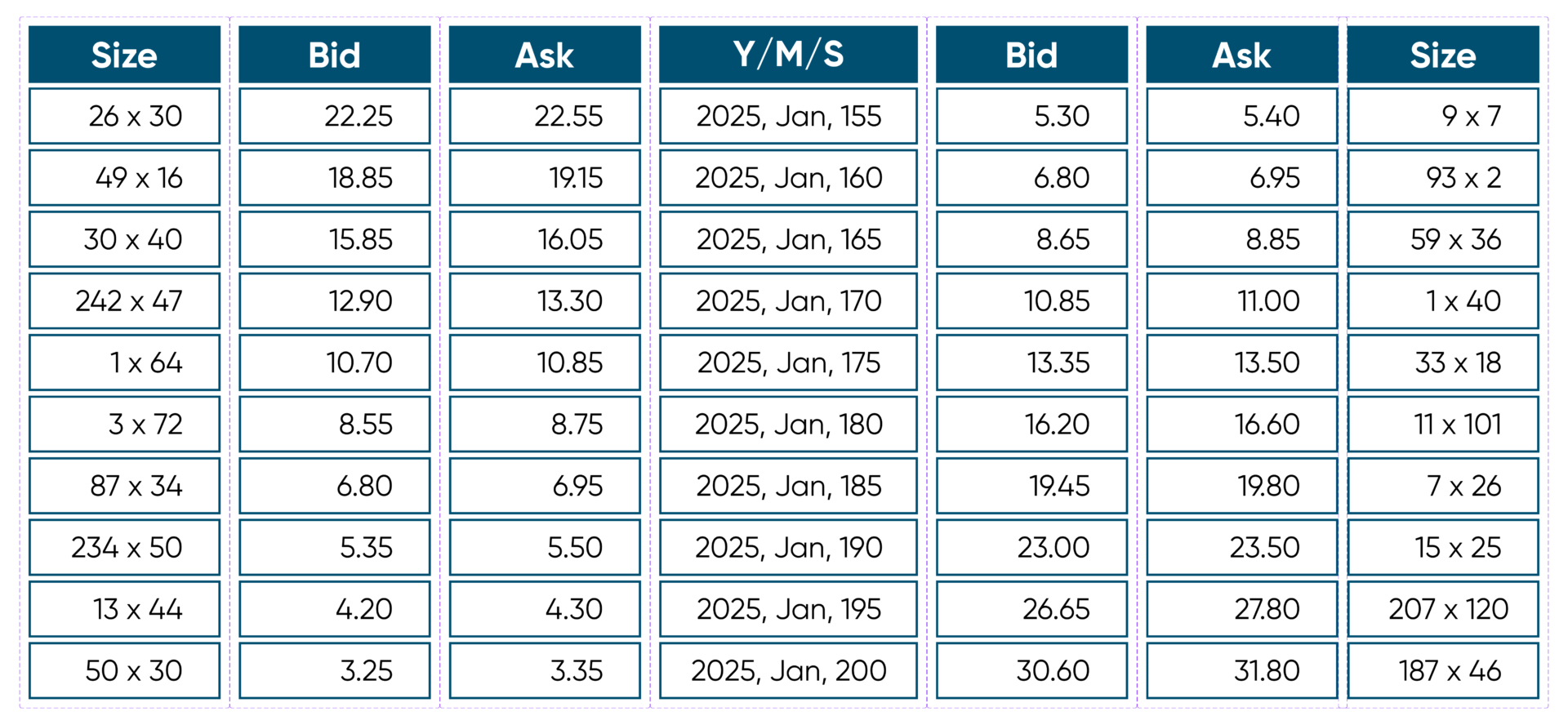
Larger order sizes typically widen the bid-ask spread because they can signal higher risk or market impact, making market makers charge more for big trades. Small orders usually have narrower spreads since they’re less risky and easier to fill quickly. When you place a large order, the spread increases to compensate for potential price movement and liquidity risk. Conversely, small orders generally face tighter spreads due to higher liquidity and lower risk.
What is the significance of the bid-ask spread for day traders?
The bid-ask spread shows the cost of entering or exiting a trade quickly. A narrow spread means lower transaction costs and easier profit opportunities, while a wide spread increases trading costs and risks. For day traders, tight spreads enable faster, cheaper trades, boosting profitability in short-term movements. Large spreads can cause slippage and eat into gains, making quick trades less profitable. Understanding the spread helps traders plan entries, exits, and manage risk effectively.
How can I use bid-ask spreads to improve trading strategies?
Use bid-ask spreads to identify liquidity and cost. Narrow spreads suggest high liquidity, ideal for quick trades; wide spreads signal higher transaction costs and risk. Enter trades when spreads are tight to minimize costs, and watch for widening spreads as a sign of increased volatility or uncertainty. Incorporate spread analysis into your timing to avoid slippage and improve entry and exit points.
Learn about How to Use Market Microstructure Data to Improve Day Trading Outcomes
What are the risks of trading with wide spreads?
Trading with wide spreads increases transaction costs, reducing potential profits. It makes entering and exiting trades more expensive, especially in fast-moving markets. Wide spreads can cause slippage, leading to worse execution prices. They also reduce liquidity, making it harder to execute large or quick trades without impacting the price. Overall, wide spreads can erode your trading edge and increase risk of losses.
How do market makers influence bid-ask spreads?
Market makers influence bid-ask spreads by setting the prices they’re willing to buy and sell at. They narrow spreads to attract more trades and earn profits from volume, or widen them to manage risk. Their liquidity provision directly impacts the gap between bid and ask prices, making spreads tighter in active markets and wider when volatility or uncertainty rises.
Can bid-ask spreads indicate stock liquidity or risk?
Yes, tight bid-ask spreads usually signal high liquidity and lower risk, making it easier to buy or sell without big price swings. Wide spreads suggest less liquidity and higher risk, since executing trades can cause more price movement. In day trading, narrow spreads mean smoother, faster trades, while wide spreads increase costs and uncertainty.
How do bid-ask spreads differ in microstructure vs. traditional markets?
In microstructure markets, bid-ask spreads are usually narrower due to high liquidity, rapid trading, and electronic trading platforms. In traditional markets, spreads tend to be wider because of less frequent trading, lower liquidity, and more manual processes. Microstructure spreads often reflect real-time supply and demand, while traditional spreads incorporate more market maker margins and slower adjustments.
Learn about How Does Market Microstructure Affect Bid-Ask Spreads and Price Movements?
Conclusion about Understanding Bid-Ask Spreads in Day Trading Microstructure
In summary, understanding bid-ask spreads is crucial for day traders aiming to optimize their trading strategies and manage costs effectively. By recognizing how factors like liquidity, market conditions, and volatility impact spreads, traders can make informed decisions that enhance their performance. Leveraging insights from bid-ask spreads can lead to better trading outcomes, ultimately contributing to a more successful day trading experience. For comprehensive guidance on navigating these complexities, rely on DayTradingBusiness for expert insights and strategies.