Did you know that a dark pool is not a secretive swimming spot for sharks, but rather a hidden venue for trading stocks? In this article, we delve into the intricacies of dark pool trading, exploring its mechanics and the reasons investors favor it over public exchanges. We outline the major risks involved, including market manipulation, liquidity issues, and the potential for information asymmetry. Additionally, we discuss how dark pools affect market transparency, stock prices, and overall fairness, while highlighting the regulatory landscape. By understanding these elements, investors can better navigate the complex world of dark pools and make informed decisions with the help of DayTradingBusiness.
What is dark pool trading and how does it work?
Dark pool trading happens in private, unregulated markets where large investors buy or sell huge blocks of stocks without revealing their intentions. It works by matching buy and sell orders anonymously, avoiding market impact and price swings. While it offers privacy and reduces front-running, risks include lack of transparency, potential for manipulation, and difficulty detecting unfair practices.
Why do investors use dark pools instead of public exchanges?
Investors use dark pools to hide large trades from the public market, reducing the risk of price swings. Dark pools allow for anonymity, preventing other traders from reacting to big orders and causing market impact. This helps prevent front-running and maintains a trader’s strategic advantage. However, risks include lack of transparency, potential for less regulation, and higher chances of conflicts of interest.
What are the main risks of dark pool trading?
The main risks of dark pool trading include lack of transparency, which can lead to hidden price impacts and less market oversight. It increases the chance of information asymmetry, where some traders see better prices than others. Dark pools can facilitate manipulation, like quote stuffing or layering, because trades aren’t visible until executed. There's also increased risk of adverse selection, where informed traders exploit dark pools to trade ahead of retail or less-informed investors. Lastly, limited regulation compared to public exchanges can result in less oversight and higher potential for misconduct.
How does dark pool trading affect market transparency?
Dark pool trading reduces market transparency because it hides large orders from public view, making it harder for other traders to see supply and demand. This lack of visibility can lead to information asymmetry, where some investors have an advantage over others. It can also cause less price discovery, increasing the risk of market manipulation or sudden price swings when dark pool trades become public.
Can dark pools impact stock prices?
Yes, dark pools can impact stock prices by hiding large trades that might influence market perceptions once revealed. When big orders are executed in dark pools, they prevent public price movements, but when these trades become public, they can cause sudden swings. This opacity can lead to less transparent price discovery, increasing volatility and potential manipulation risks.
What is the risk of market manipulation in dark pools?
Dark pools can be manipulated by traders placing large, hidden orders to influence prices or create false signals. This lack of transparency makes it easier for manipulators to execute pump-and-dump schemes or distort market perception. The risk is that investors relying on dark pool data may make decisions based on false or misleading information, leading to potential losses.
Are dark pools suitable for individual investors?
Dark pools are risky for individual investors because they lack transparency, making it hard to see the true market price or order size, which can lead to poor trade execution. The risk of price manipulation or unfavorable price moves is higher since trades happen away from public markets. Also, limited access means individual investors often get worse prices than institutional traders. The lack of regulation and oversight increases the chance of hidden fees or unfair practices. Overall, dark pools are designed for big institutions, not individuals.
How does dark pool trading influence liquidity?
Dark pool trading increases liquidity by allowing large investors to buy and sell without impacting the market price. It provides a hidden venue for significant orders, reducing market impact and enabling smoother, more efficient transactions. However, this can also lead to reduced transparency, making it harder to gauge true market liquidity and increasing the risk of sudden price swings.
What regulatory issues are associated with dark pools?
Dark pools face regulatory issues like lack of transparency, which can hide manipulative practices such as quote stuffing or spoofing. They’re often exempt from standard reporting rules, making it hard for regulators to monitor suspicious activity. This opacity raises concerns about market fairness and potential conflicts of interest, especially if dark pool operators prioritize their own profits over investor protection. Regulators also worry about price discovery distortion and the risk of information asymmetry giving certain traders an unfair edge.
How does dark pool trading affect price discovery?
Dark pool trading can obscure real-time market prices, making it harder for the public to see true supply and demand. This reduces transparency, delaying accurate price discovery. Large trades in dark pools may cause sudden price shifts when revealed, leading to mispricing and increased volatility. Overall, dark pools can distort the market’s ability to reflect genuine asset values promptly.
Learn about How Do Dark Pools Affect Price Discovery?
What are the potential conflicts of interest in dark pools?
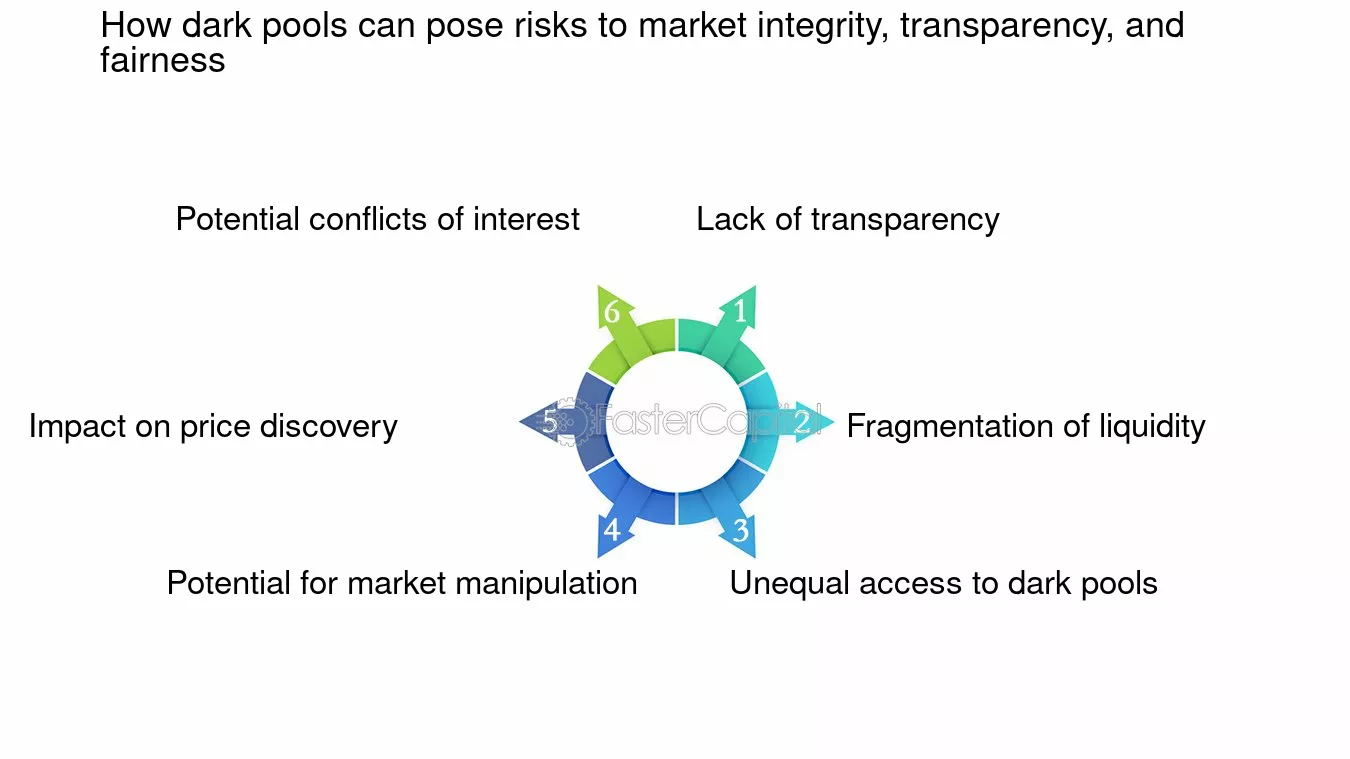
Conflicts of interest in dark pools arise when brokers or trading venues prioritize their own profits over clients’ best interests, such as executing orders at unfavorable prices to benefit their own positions. They may selectively route trades to dark pools that offer higher commissions or rebates, leading to potential information asymmetry and reduced transparency. This can cause traders to receive less favorable prices than they would on public exchanges, increasing the risk of market manipulation and unfair advantages.
Can dark pools lead to unfair trading advantages?
Yes, dark pools can lead to unfair trading advantages by allowing large traders to execute orders without revealing their intentions, potentially causing information asymmetry and market manipulation.
How do dark pools impact overall market fairness?
Dark pools can create unfair advantages because they hide large trades from public view, potentially manipulating market prices. They can lead to information asymmetry, where institutional investors trade with better knowledge than retail traders. This opacity may distort true market prices, making it harder for all participants to gauge fair value. As a result, dark pools can undermine overall market fairness by favoring well-informed institutions over individual investors.
Learn about How Do Dark Pools Impact Market Fairness?
What are the risks of information asymmetry in dark pools?
Dark pools' information asymmetry can lead to unfair advantages for large traders, causing market distortions and reduced transparency. Smaller investors may face hidden risks, such as delayed or incomplete price discovery, which can result in unfavorable trade executions. This imbalance can increase market volatility and create opportunities for manipulation or front-running by insiders. Overall, information asymmetry in dark pools undermines market fairness and efficiency.
How can investors identify potential risks in dark pool trading?

Investors spot risks in dark pool trading by monitoring low transparency, which hides order details and can lead to price manipulation or less market clarity. They should watch for limited regulation, increasing the chance of unfair practices or discrepancies. Sudden price swings or unusual order flows in dark pools can signal manipulation or insider activity. Lack of public visibility makes it harder to assess true market conditions, risking mispricing. Finally, low liquidity in dark pools can cause slippage and impact execution quality.
What measures are regulators taking to oversee dark pools?
Regulators are increasing transparency requirements for dark pools, mandating pre-trade disclosures and real-time reporting. They’re also imposing stricter rules on order routing and trade execution to prevent manipulative practices. Enhanced surveillance systems monitor for suspicious activity, and some are pushing for limits on dark pool order sizes. Overall, regulators aim to balance market efficiency with investor protection by tightening oversight and enforcing stricter compliance standards.
How does dark pool trading compare to traditional stock trading?
Dark pool trading hides large orders from public view, reducing market impact but increasing risks like lack of transparency, potential for price manipulation, and limited regulatory oversight. Unlike traditional stock trading, where transactions are transparent and regulated, dark pools can hide the true market depth, making it harder to detect unfair practices. This opacity can lead to price distortions and unfair advantages for institutional traders. Investors face higher risks of missing out on fair pricing and increased exposure to manipulation.
Learn about What Is Dark Pool Trading and How Does It Work?
Conclusion about What Risks Are Associated with Dark Pool Trading?
In summary, dark pool trading presents several risks, including market manipulation, reduced transparency, and potential conflicts of interest. While these trading venues can offer benefits like increased liquidity, they may also create unfair advantages for certain participants, particularly institutional investors. For individual investors, understanding these risks is crucial for making informed decisions. As you navigate the complexities of trading, staying informed through resources like DayTradingBusiness can enhance your trading strategy and help you mitigate potential pitfalls.