Did you know that high-frequency trading (HFT) can execute orders in microseconds, faster than you can say "buy low, sell high"? In the world of HFT day trading, navigating legal requirements is just as critical as mastering trading strategies. This article dives into the essential legal considerations for HFT in the U.S. and Europe, covering SEC regulations, compliance issues, licensing requirements, and the implications of market manipulation laws. You'll learn how to ensure compliance with insider trading laws, reporting obligations, and even the tax implications of your trading profits. Plus, we’ll explore the role of exchanges and regulatory bodies like FINRA in overseeing HFT activities. Avoid legal pitfalls and sharpen your trading approach with insights from DayTradingBusiness to stay ahead in this fast-paced market.
What are the legal requirements for high-frequency trading (HFT) in the U.S.?
High-frequency trading (HFT) in the U.S. must comply with several legal requirements:
1. Registration: HFT firms must register with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and become members of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA).
2. Compliance with Regulations: HFT strategies must adhere to regulations such as the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and the Dodd-Frank Act, which promote fair trading practices and market integrity.
3. Reporting and Recordkeeping: Firms are required to maintain detailed records of trades and reporting, which include timestamps and execution data, to ensure transparency.
4. Market Access: HFT firms need to have proper market access arrangements and must comply with rules regarding direct market access (DMA) to prevent market manipulation.
5. Risk Management: Implementing robust risk management systems is necessary to monitor trading activities and prevent excessive risk exposure.
6. Anti-Money Laundering (AML): Compliance with AML regulations is mandatory, requiring firms to establish policies to detect and report suspicious activities.
7. Order Execution: HFT firms must follow "best execution" obligations, ensuring trades are executed at the best available prices, maintaining fairness for all market participants.
These requirements are aimed at promoting transparency, fairness, and stability in the markets.
How does SEC regulation affect day trading strategies?
SEC regulation impacts day trading strategies by imposing rules on reporting, pattern day trading, and margin requirements. Traders need to maintain a minimum balance of $25,000 to execute more than three day trades within five business days, which influences their trading frequency and strategy. Additionally, regulations on short selling and insider trading can affect decision-making and risk management. Compliance with these rules is crucial to avoid penalties and ensure sustainable trading practices.
What are the key compliance issues for HFT firms?
Key compliance issues for high-frequency trading (HFT) firms include:
1. Market Manipulation: Avoiding practices like spoofing and layering that distort market prices.
2. Regulatory Reporting: Ensuring accurate and timely reports to regulators, including trade data and risk assessments.
3. Risk Management: Implementing robust risk controls to prevent excessive losses and maintain capital adequacy.
4. Data Security: Protecting sensitive trading algorithms and client data from breaches.
5. Anti-Money Laundering (AML): Complying with AML regulations to prevent illicit activities.
6. Best Execution: Meeting obligations to execute trades at the best available prices for clients.
7. Compliance with MiFID II: Adhering to European regulations governing trading practices and transparency.
Addressing these issues is crucial for legal compliance and maintaining market integrity.
How can traders ensure they meet legal obligations in HFT?
Traders can ensure they meet legal obligations in high-frequency trading (HFT) by staying updated on regulations from bodies like the SEC and CFTC. Implement robust compliance programs to monitor trading activities and transaction reporting. Use technology to maintain transparent records and ensure accurate reporting of trades. Engage legal experts specializing in financial regulations to review trading strategies and practices. Regularly conduct audits to identify and rectify compliance gaps. Lastly, participate in industry forums to stay informed about evolving legal standards.
What are the implications of market manipulation laws for day traders?
Market manipulation laws can significantly impact day traders by imposing strict regulations on trading practices. Day traders must avoid practices like spoofing, wash trading, or any deceptive tactics that could distort market prices. Violating these laws can lead to severe penalties, including fines and bans from trading. Compliance is crucial; traders should be transparent in their transactions and ensure their strategies align with legal standards. Understanding these implications helps day traders mitigate risks and maintain their trading licenses.
Are there specific licensing requirements for HFT traders?
Yes, high-frequency trading (HFT) traders must comply with specific licensing requirements. In the U.S., they typically need to register as broker-dealers with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and may also require membership in a self-regulatory organization like FINRA. Additionally, firms engaging in HFT often need to meet capital requirements and adhere to regulatory reporting standards. Always check local regulations, as requirements can vary by jurisdiction.
How do insider trading laws impact high-frequency trading?
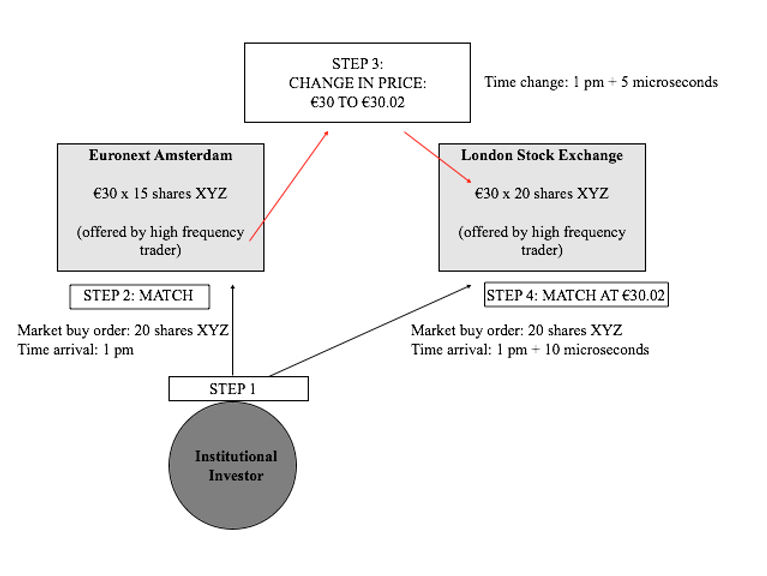
Insider trading laws significantly impact high-frequency trading (HFT) by prohibiting the use of non-public, material information for trading. HFT firms must ensure their algorithms do not exploit insider information, as violations can lead to severe penalties, including fines and imprisonment. Compliance with these laws requires robust surveillance systems to detect potential insider trading, affecting how HFT strategies are developed and executed. Ultimately, these regulations aim to maintain market integrity, ensuring a level playing field for all traders.
What reporting obligations do HFT firms have?
High-frequency trading (HFT) firms must adhere to several reporting obligations, including:
1. Transaction Reporting: Firms must report trades to exchanges and regulatory bodies, detailing transaction specifics like price, volume, and time.
2. Market Surveillance: They need to provide data for market surveillance, ensuring compliance with regulations like the SEC's Rule 15c3-5.
3. Risk Management Reporting: HFT firms must maintain and report risk assessments, demonstrating their ability to manage market risks effectively.
4. Position Reporting: They may be required to report large positions to regulators, particularly if exceeding thresholds set by regulations like the CFTC’s large trader reporting.
5. Compliance with MiFID II: In Europe, HFT firms must comply with MiFID II, which includes detailed reporting on algorithmic trading and order execution.
6. Tax Reporting: Accurate reporting for tax purposes is essential, including profits and losses from trading activities.
These obligations ensure transparency and integrity in the markets where HFT firms operate.
How does the MiFID II regulation influence day trading in Europe?
MiFID II regulation impacts day trading in Europe by increasing transparency and investor protection. It mandates greater disclosure of trading costs and enhances reporting requirements, which can affect trading strategies. High-frequency traders must comply with stricter rules on algorithmic trading and best execution practices, potentially altering their operational efficiencies. Additionally, limits on leverage and more rigorous capital requirements can restrict the amount of capital available for day trading. Overall, MiFID II seeks to create a fairer trading environment but adds compliance burdens that can influence trading activities.
What are the tax implications of HFT day trading profits?
HFT day trading profits are generally taxed as short-term capital gains, which means they are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. If you're classified as a trader by the IRS, you might qualify for trader tax status, allowing for potential deductions on trading expenses. Be aware of wash sale rules, which can affect your ability to deduct losses. Always consult a tax professional for personalized advice based on your trading activity.
Learn about Tax Implications of Day Trading in Different Countries
How can traders avoid legal pitfalls in algorithmic trading?
Traders can avoid legal pitfalls in algorithmic trading by adhering to these key practices:
1. Understand Regulations: Familiarize yourself with relevant laws, including SEC and FINRA regulations, to ensure compliance.
2. Use Reliable Data Sources: Ensure that your algorithms rely on accurate and authorized data to avoid issues related to market manipulation.
3. Implement Risk Controls: Build safeguards within your algorithms to prevent excessive trading and mitigate the risk of market disruptions.
4. Conduct Regular Audits: Regularly review and audit your trading strategies to identify and address any potential compliance issues.
5. Document Everything: Keep detailed records of your trading strategies, data sources, and any communications related to your trading activities.
6. Seek Legal Advice: Consult with legal experts who specialize in securities law to navigate complex regulations specific to algorithmic trading.
7. Stay Updated: Continuously monitor changes in laws and regulations that may impact your trading practices.
By following these steps, traders can significantly reduce the risk of legal issues in high-frequency trading.
What role do exchanges play in regulating HFT activities?
Exchanges regulate high-frequency trading (HFT) activities by setting rules for trading practices, ensuring fair access to market data, and implementing surveillance systems to monitor trading behavior. They establish parameters like minimum tick sizes and limit order types to prevent market manipulation. Additionally, exchanges may require HFT firms to adhere to specific reporting standards and risk management practices, enhancing transparency and stability in the market.
How does the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) oversee HFT trading?
FINRA oversees high-frequency trading (HFT) by enforcing regulations that ensure fair practices and transparency. They monitor trading activities, requiring firms to report their trades and maintain records for regulatory review. FINRA also conducts audits and investigations to detect manipulative behaviors, like quote stuffing or spoofing. Additionally, they provide guidance on compliance with existing trading rules and collaborate with other regulatory bodies to enhance oversight.
What are the consequences of non-compliance in high-frequency trading?
Non-compliance in high-frequency trading (HFT) can lead to severe consequences, including hefty fines from regulatory bodies, loss of trading licenses, and legal action. Firms may face increased scrutiny and audits, damage to their reputation, and potential criminal charges for market manipulation. Additionally, non-compliance can result in significant financial losses due to penalties and trading halts, impacting overall business viability.
How do anti-money laundering laws affect day trading practices?
Anti-money laundering (AML) laws require day traders to comply with regulations aimed at preventing financial crimes. Traders must verify their identity, report suspicious transactions, and maintain accurate records. This can limit anonymity in trading and increase compliance costs. Failure to meet these regulations can lead to penalties, including fines and restrictions on trading activities. Overall, AML laws create a framework that ensures transparency and accountability in day trading practices.
Learn about How Do Anti-Money Laundering Laws Affect Day Traders?
What is the impact of trade surveillance on HFT strategies?
Trade surveillance significantly impacts high-frequency trading (HFT) strategies by enforcing compliance with regulations and monitoring market manipulation. It requires HFT firms to implement robust systems to detect anomalies, ensuring their strategies do not inadvertently cross legal boundaries. This oversight can lead to increased operational costs and necessitate adjustments in algorithms to avoid triggering alerts. Additionally, effective trade surveillance may enhance market integrity, benefiting HFT firms by fostering a fair trading environment. Overall, HFT strategies must adapt to the evolving landscape of legal considerations shaped by trade surveillance practices.
Conclusion about Legal Considerations for HFT Day Trading
In conclusion, navigating the legal landscape of high-frequency trading (HFT) is essential for traders seeking to optimize their strategies while remaining compliant. Understanding SEC regulations, reporting obligations, and market manipulation laws is crucial to avoid legal pitfalls. Additionally, awareness of licensing requirements and the influence of regulations like MiFID II can significantly impact trading practices. By staying informed and proactive, traders can effectively manage their legal responsibilities in HFT. For detailed guidance and support, DayTradingBusiness is here to help you succeed in your trading journey.
Learn about What legal considerations are there for automated day trading systems?