Did you know that the average person spends about 6 months of their life waiting for red lights to turn green? Similarly, in trading, waiting for the right position size can be the key to a profitable journey. In this article, we delve into the critical role of position sizing in risk management, covering its definition, significance, and impact on overall portfolio risk. We’ll explore methods for determining optimal position size, the influence of account size and risk tolerance, and the effects of stop-loss levels and volatility. Additionally, we discuss the risks of improper sizing, the benefits of proper position sizing for long-term success, and essential tools for calculation. Finally, we look at how to adapt position sizes across different asset classes and changing market conditions. Join us at DayTradingBusiness as we equip you with the knowledge to make informed trading decisions.
What is position sizing in trading and investing?
Position sizing in trading and investing is determining how much capital to allocate to a single trade or investment. It controls risk by ensuring each position aligns with your overall risk tolerance, preventing large losses. Proper position sizing helps balance potential gains against potential losses, making your risk management more effective. For example, risking 1% of your account on each trade means your position size adjusts based on your account size and stop-loss level.
Why is position sizing crucial for risk management?
Position sizing determines how much you invest in each trade, directly controlling your potential losses. It limits risk exposure, preventing a single bad trade from wiping out your account. Proper sizing aligns your trades with your risk tolerance, ensuring consistent, manageable losses. Without it, even a small mistake can lead to significant financial damage, making risk management ineffective.
How does position size affect overall portfolio risk?
Position size directly impacts portfolio risk by determining how much capital is exposed to each trade. Larger positions increase potential gains but also amplify losses, raising overall risk. Smaller positions limit downside exposure, making the portfolio more resilient to market swings. Proper position sizing balances risk and reward, preventing a single trade from significantly damaging the entire portfolio.
What are common methods to determine optimal position size?
Common methods to determine optimal position size include using a fixed percentage of your trading capital, like risking 1-2% per trade, and calculating position size based on stop-loss distance to limit potential losses. The Kelly Criterion adjusts size by considering win probability and payoff, maximizing growth while managing risk. Another approach is the volatility-based method, where position size is scaled according to the asset’s volatility to normalize risk exposure. Always match position size to your risk tolerance and the specific trade setup.
How does account size influence position sizing decisions?
Account size determines how much capital you can risk per trade, shaping your position size. Larger accounts allow bigger positions without risking too much of your capital, while smaller accounts require smaller trades to stay within risk limits. The goal is to keep risk consistent—typically 1-2% of your account—so your position size adjusts to account size to protect your overall capital.
What role does risk tolerance play in position sizing?
Risk tolerance determines how much of your capital you're willing to risk on a trade, guiding your position size. If you have a high risk tolerance, you'll take larger positions; if low, you'll keep positions smaller. It helps balance potential gains with acceptable losses, ensuring you don’t overexpose yourself. Essentially, your risk tolerance acts as a limit, shaping how big or small each trade is within your overall risk management plan.
How can stop-loss levels impact position size?
Stop-loss levels directly limit potential losses, so tighter stops reduce risk per trade and allow for larger position sizes. Conversely, wider stops increase risk per trade, forcing smaller positions to stay within acceptable risk limits. Properly setting stop-loss levels ensures you don’t overextend your position size, balancing risk and reward.
What is the relationship between leverage and position sizing?
Leverage amplifies your position size's impact on risk. Higher leverage allows bigger positions with less capital, increasing potential gains but also risk. Proper position sizing adjusts for leverage to control exposure, ensuring you don’t take on more risk than your account can handle. Essentially, leverage determines how much you can trade, while position sizing decides how much of your capital to commit within that limit. Balancing both keeps risk aligned with your trading plan.
How does volatility affect how much I should trade?
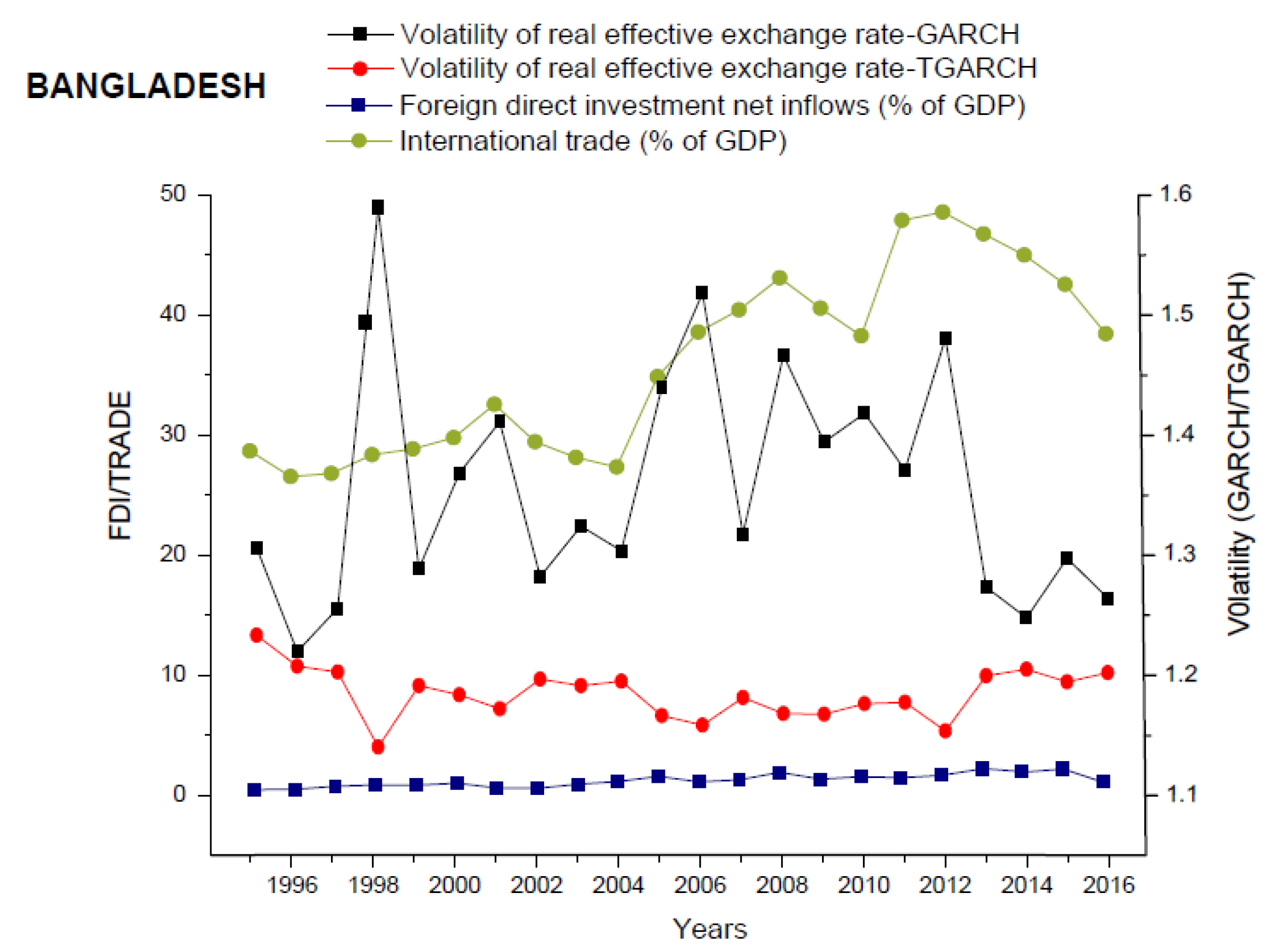
Higher volatility means larger price swings, so you should reduce your trade size to avoid excessive risk. Lower volatility allows for bigger positions since price moves are smaller and less risky. Adjust your position size based on volatility to keep your risk levels consistent and protect your capital.
What are the risks of over-sizing or under-sizing positions?
Over-sizing positions increases the risk of large losses, potentially wiping out your account during adverse moves. Under-sizing limits potential gains and may lead to missed opportunities, but it keeps risk manageable. Both errors distort your risk-reward balance and can cause emotional stress, leading to poor trading decisions. Proper position sizing aligns risk with your capital and trading plan, preventing catastrophic losses or underperformance.
How can position sizing improve long-term trading success?
Position sizing controls how much you risk on each trade, preventing large losses that can wipe out your account. It helps you stay consistent, so you can survive losing streaks and grow steadily. By adjusting position size based on market volatility and account size, you protect your capital and maintain a balanced risk-reward ratio. Proper sizing reduces emotional trading, keeps risk manageable, and supports sustainable long-term growth.
Learn about How to Incorporate Position Sizing into Your Trading Plan
What tools or formulas can help calculate position size?
Tools like the fixed fractional method, Kelly Criterion, and percentage risk calculators help determine position size. Formulas include: position size = (account balance × risk per trade) ÷ stop-loss distance. Use online position size calculators for quick, accurate results.
How does diversification relate to position sizing?
Diversification spreads your investments across different assets to reduce risk, while position sizing determines how much of your capital you allocate to each trade. Proper position sizing ensures no single trade can wipe out your portfolio, complementing diversification by controlling individual trade risk. Together, they balance overall risk: diversification limits exposure to specific asset risks, and position sizing manages the size of each position within that framework.
What mistakes should traders avoid with position sizing?
Traders should avoid risking too much on a single trade, typically more than 1-2% of their capital. Don’t ignore market volatility; larger swings require smaller positions. Avoid doubling down after losses—this increases risk unnecessarily. Never base position size on emotions or guesses, stick to a plan. Overestimating your account’s ability to handle big moves leads to bigger losses. Also, avoid ignoring stop-loss levels; improper sizing can make stops too tight or too wide.
How does position sizing vary across different asset classes?
Position sizing varies based on asset volatility, liquidity, and risk profile. In stocks, traders often use a fixed percentage of capital, like 1-2%, to limit exposure. For forex, due to high leverage, position sizes are smaller relative to account size to avoid overexposure. Commodities like gold or oil require adjusting size based on their price swings and market liquidity. Bonds tend to allow larger positions because they’re less volatile, but risk limits still apply. Overall, higher volatility assets demand smaller positions to manage risk, while more stable assets permit larger sizes.
How to adjust position size during changing market conditions?
Adjust position size based on current market volatility and your risk tolerance. Increase size in stable conditions with low volatility, and reduce it during high volatility or unpredictable markets. Use tools like ATR or volatility indicators to gauge market risk and scale your trades accordingly. Always stick to a fixed percentage of your capital per trade to maintain consistent risk levels, adjusting that percentage if market conditions shift.
Learn about How to Adjust Position Size During Volatile Markets
Conclusion about The Role of Position Sizing in Overall Risk Management
Incorporating effective position sizing is essential for robust risk management in trading. By understanding its impact on portfolio risk, account size, and individual risk tolerance, traders can make informed decisions that enhance their overall strategy. Implementing sound position sizing techniques not only mitigates potential losses but also cultivates long-term success. For those looking to deepen their trading knowledge, DayTradingBusiness offers valuable insights and resources tailored to mastering these concepts.
Learn about The role of position sizing in controlling stop-loss risk