Did you know that even the best traders can lose money faster than a cheetah on roller skates? To mitigate losses, understanding backtesting of stop-loss risk management methods is crucial. This article dives into why backtesting is essential for developing effective stop-loss strategies, enhancing overall risk management, and identifying optimal stop-loss levels. We’ll explore the benefits of backtesting, common pitfalls to avoid, and the data required for accurate assessments. Additionally, we’ll discuss how backtesting can highlight weaknesses in your strategies and provide best practices for ongoing improvement. Get ready to sharpen your trading skills with insights from DayTradingBusiness!
Why is backtesting stop-loss strategies important?
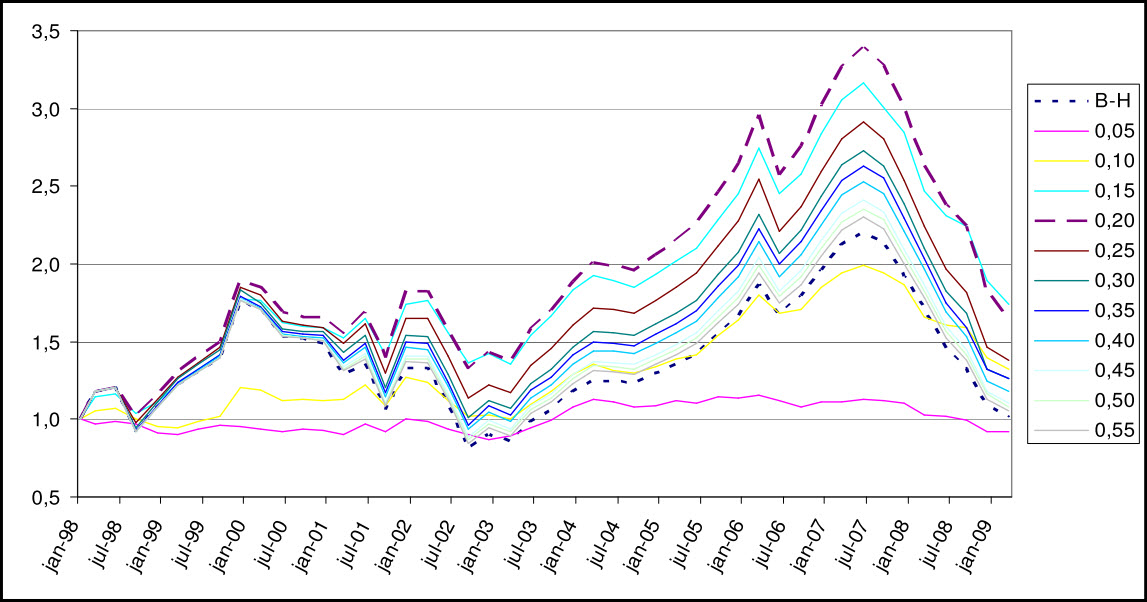
Backtesting stop-loss strategies shows if they effectively limit losses and protect profits. It reveals how different methods perform across market conditions. Without backtesting, you risk using stop-loss rules that may cause unnecessary exits or large losses. It helps optimize your approach, making your risk management more reliable. Essentially, it ensures your stop-loss strategy works before risking real money.
How does backtesting improve risk management?
Backtesting improves risk management by revealing how stop-loss strategies perform during different market conditions. It helps identify potential weaknesses and optimize stop-loss levels to minimize losses. By analyzing past data, traders can refine their approach, reduce emotional decision-making, and build confidence in their risk controls. Essentially, backtesting ensures your stop-loss method is robust, reliable, and tailored to your trading style.
What are the benefits of backtesting stop-loss methods?
Backtesting stop-loss methods shows how they perform historically, helping you identify effective risk limits. It reveals potential losses, improves decision-making, and boosts confidence in your strategy. By analyzing past data, you can refine stop-loss placement, prevent big losses, and increase overall trading consistency.
How can backtesting help identify effective stop-loss levels?
Backtesting shows how different stop-loss levels would have performed historically, revealing which ones minimize losses and protect gains. It helps you identify the stop-loss placements that prevent big drawdowns while allowing profitable trades to run. By analyzing past data, you can fine-tune your stop-loss strategy to balance risk and reward effectively.
What are common pitfalls in backtesting stop-loss strategies?
Common pitfalls in backtesting stop-loss strategies include ignoring market volatility, overfitting parameters to past data, using insufficient sample sizes, neglecting transaction costs and slippage, and assuming perfect execution. Relying solely on historical data without considering changing market conditions can mislead. Over-optimizing for past performance may not work in real-time. Failing to incorporate realistic trading environments skews results. These mistakes lead to strategies that look good on paper but fail in live trading.
How do different stop-loss techniques perform in backtests?
Different stop-loss techniques vary in backtest performance; trailing stops often reduce losses during volatile markets, while fixed percentage stops may cut profits prematurely. Backtests show that adaptive stops, like volatility-based or ATR stops, better protect gains and limit drawdowns compared to static methods. The effectiveness depends on market conditions and asset volatility, with some techniques outperforming others in specific scenarios.
What data is needed to backtest stop-loss systems?
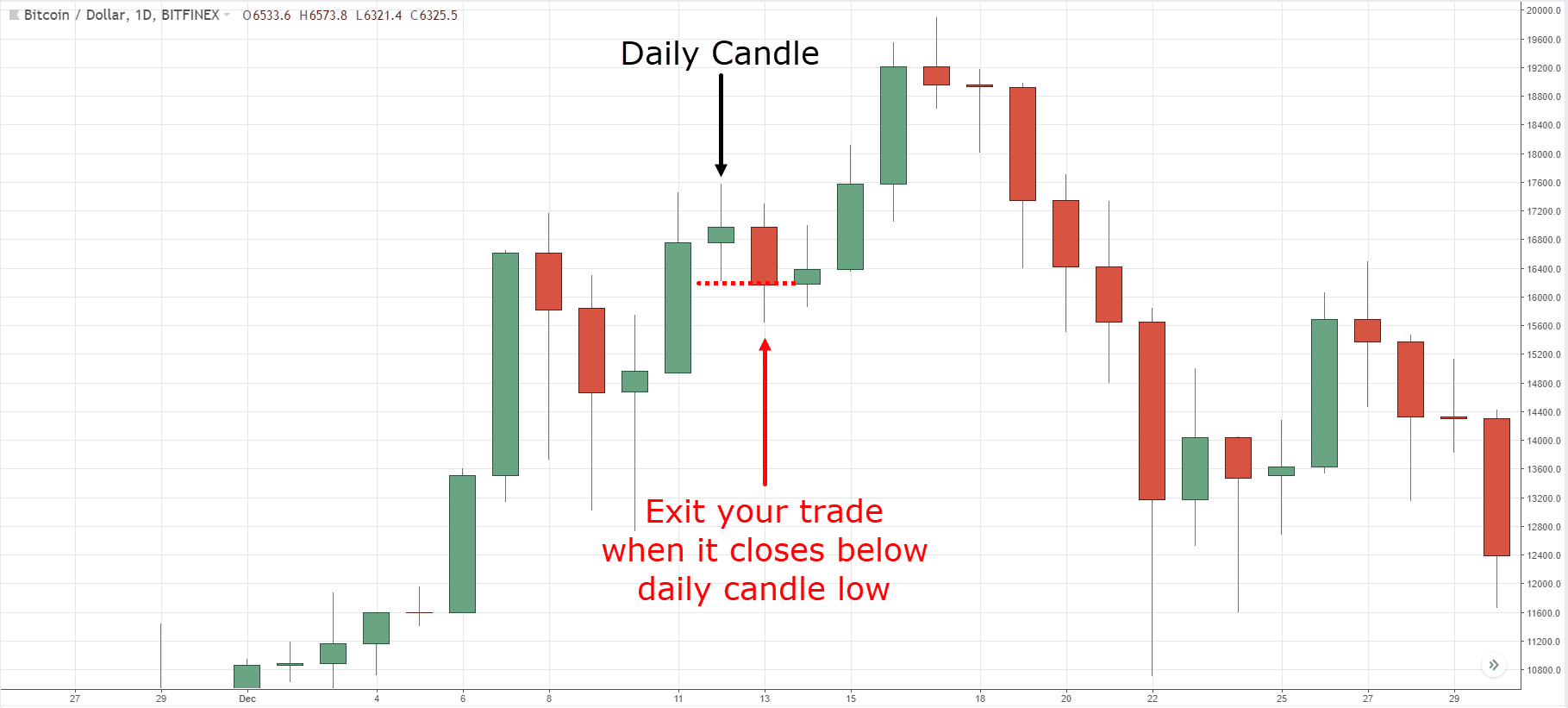
Historical price data, including open, high, low, and close prices, is essential. You also need trade execution data, such as order entry and exit points, to simulate real conditions. Volatility and volume data help assess market behavior during different periods. Additionally, access to past market events and news can improve accuracy by understanding how stops would react in various scenarios.
How does backtesting validate stop-loss risk management?
Backtesting validates stop-loss risk management by simulating how the stop-loss strategy would have performed over historical data. It reveals whether the stop-loss levels effectively limit losses without causing premature exits. By analyzing past trades, traders can see if the stop-loss method balances risk and reward, ensuring it’s reliable before applying it live.
Can backtesting reveal weaknesses in stop-loss strategies?
Yes, backtesting can reveal weaknesses in stop-loss strategies by showing how they perform across different market conditions, highlighting scenarios where they fail to protect profits or prevent losses.
What metrics should be used in backtesting stop-loss methods?
Use metrics like the average loss per trade, maximum drawdown, profit factor, win rate, risk-reward ratio, and the Sharpe ratio. Track how often stop-losses prevent larger losses, the overall profitability, and the consistency of results. These indicators show if the stop-loss method effectively manages risk without sacrificing too much profit.
How often should you backtest your stop-loss techniques?
Backtest your stop-loss techniques regularly, at least quarterly, to ensure they adapt to market changes and remain effective.
What role does historical market data play in backtesting?
Historical market data is essential in backtesting stop-loss risk management methods because it provides real past price movements to test how a stop-loss strategy would have performed. It helps identify potential weaknesses, optimize stop-loss levels, and assess the strategy's effectiveness under different market conditions. Without accurate historical data, backtesting can't reliably predict how a stop-loss approach will behave in live trading.
How does backtesting compare to forward testing for stop-loss?
Backtesting evaluates how a stop-loss strategy would have performed on historical data, helping identify effective risk management methods. Forward testing, in contrast, tests the stop-loss on live or simulated future trades, revealing real-time performance and adjustments needed. Backtesting offers insights into past effectiveness, while forward testing confirms if the stop-loss works in current market conditions. Both are essential: backtesting for strategy development, forward testing for validation.
What are best practices for accurate backtesting of stop-loss methods?
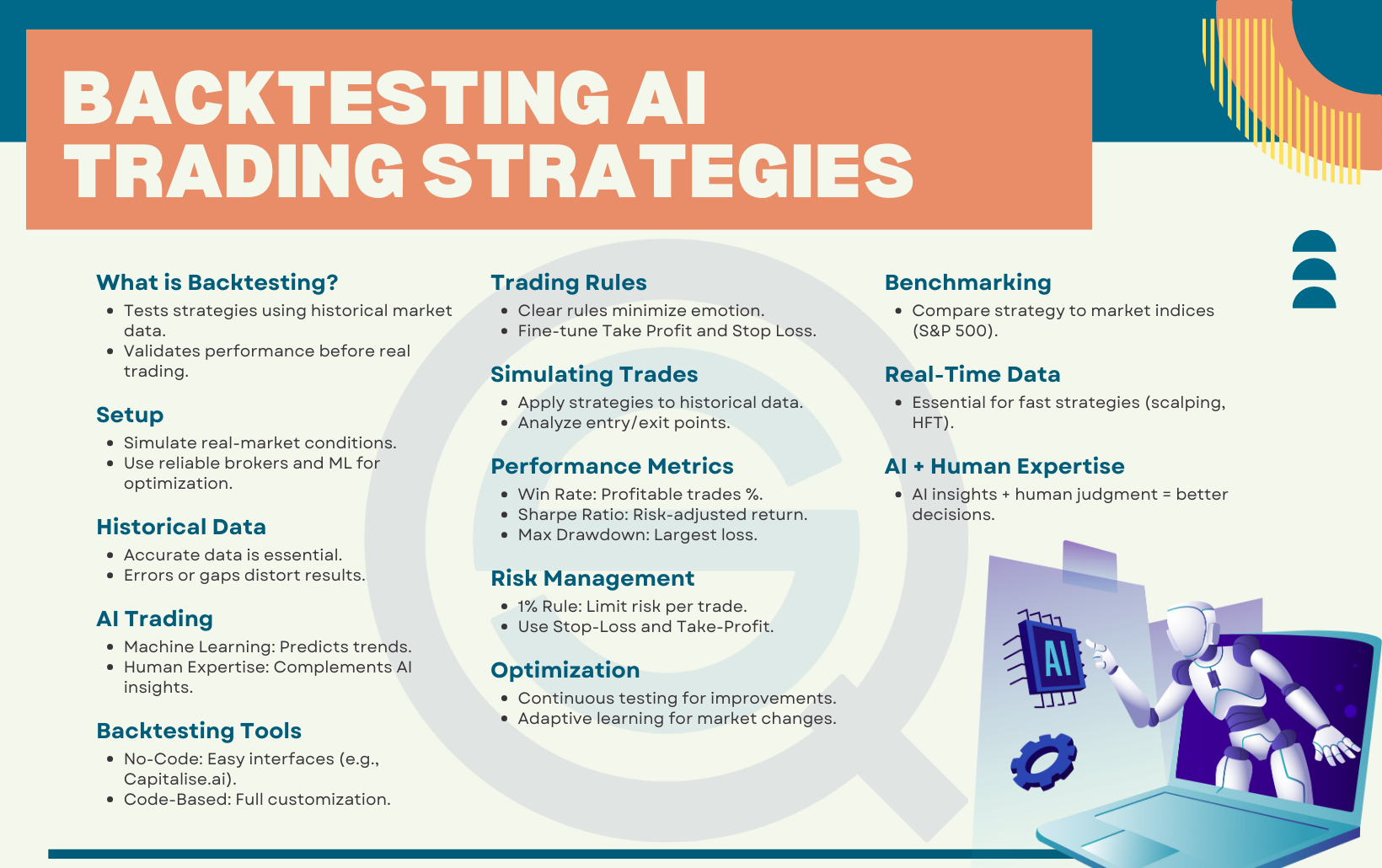
Use historical data that reflects current market conditions. Test your stop-loss strategies across different market scenarios, including trending and sideways markets. Avoid overfitting by not tailoring stops too tightly to specific past data. Incorporate realistic trading costs and slippage. Validate results with out-of-sample data to ensure robustness. Regularly update and review your backtests to adapt to changing market dynamics. Use multiple stop-loss methods to compare performance and avoid relying on a single approach.
How can backtesting help optimize your stop-loss parameters?
Backtesting helps optimize stop-loss parameters by revealing which levels maximize gains and minimize losses based on past data. It shows how different stop-loss settings would have performed historically, allowing you to fine-tune your approach. By analyzing these results, you identify the most effective stop-loss distances, balancing risk and reward. This process helps prevent emotional decisions and improves your overall risk management strategy.
Conclusion about The importance of backtesting stop-loss risk management methods
Incorporating backtesting into your stop-loss risk management strategies is crucial for effective trading. It enhances risk assessment, identifies optimal stop-loss levels, and reveals potential weaknesses in your methods. Regular backtesting, alongside historical market data, allows traders to refine their techniques and improve overall performance. By following best practices, you can ensure accuracy and maximize the benefits of your stop-loss strategies. For comprehensive support and insights into backtesting and trading, DayTradingBusiness is here to help you navigate the complexities of the market.